

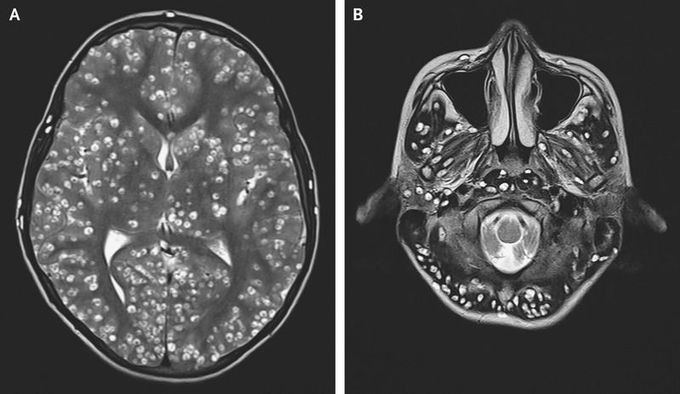
Disseminated Cysticercosis
An 18-year-old man presented to the emergency department with generalized tonic–clonic seizures. His parents reported that he had been having pain in the right groin for 1 week. On physical examination, the patient was confused. He had swelling over the right eye and tenderness in the right testis. Magnetic resonance imaging of the head showed numerous well-defined cystic lesions throughout the cerebral cortex (Panel A) and the brain stem and cerebellum (Panel B) that were consistent with neurocysticercosis. Well-defined cysts that contained echogenic nodules were seen on ultrasonography of the eye and the right testis. Western blot analysis and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay showed positive results for serum cysticercosis IgG antibody. In the context of high cyst burden, treatment with antiparasitic medications can worsen inflammation and cerebral edema, and in the presence of ocular lesions, inflammation can lead to loss of vision. Therefore, antiparasitic medications were not administered in this case. Despite treatment with dexamethasone and antiepileptic medications, the patient died 2 weeks later.
Taenia solium (tapeworm) the ova which contaminate people come from undercooked pork or feces of other patients



