
SYRINGOMYELIA
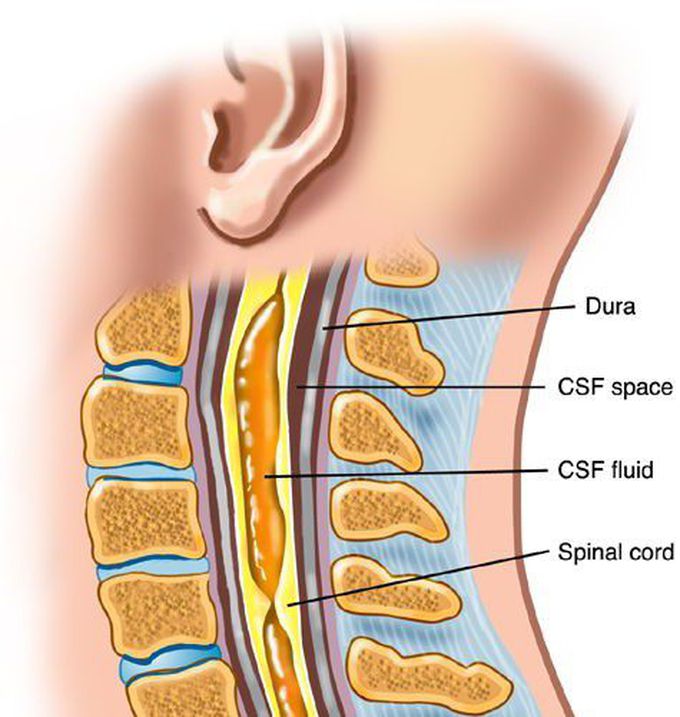
Syringomyelia is a rare disorder in which a fluid-filled cyst forms within your spinal cord. This cyst is referred to as a syrinx. Damage to the spinal cord caused by a syrinx can lead to symptoms such as progressive pain, stiffness, and weakness in the back, shoulders, arms and legs. But what causes syringomyelia? 1. Malformation of the brain known as Chiari type 1 malformation (CM1). CM1 occurs where the brain joins the spinal cord. In this malformation, the brainstem lies lower than normal. Located at the back of the brainstem is the cerebellum. Often with CM1, the bases of the lobes of the cerebellum, or the cerebellar tonsils, protrude from the skull (foramen magnum) and into the spinal canal. If you have CM1, your surgeon may suggest surgery to expand the base of your skull and the covering of your brain. This will take pressure off your spinal cord and your brain. The normal flow of cerebrospinal fluid should be restored. 2.Syringomyelia with fourth ventricle communication. Approximately 10% of syringomyelia cases are of this type. The communication is visible on MRI. In some cases a blockage of CSF circulation occurs: a shunt operation may be the best therapeutic option for these patients. 3. Syringomyelia due to spinal cord injury. Fewer than 10% of syringomyelia cases are of this type. Mechanisms of injury include: - spinal trauma - radiation necrosis - hemorrhage from aneurysm rupture or arteriovenous malformation or in a tumour bed - infection (spinal abscess, human immunodeficiency virus, transverse myelitis) - cavitation following ischaemic injury or degenerative disease 4. Idiopathic Syringomyelia Idiopathic syringomyelia has an unknown cause and cannot be classified under any of the previous categories. What are the symptoms of syringomyelia? - a progressive weakness and pain in the back, shoulders, arms, or legs - an inability to feel hot or cold -a loss of pain sensation - difficulty walking - bowel and bladder function problems - facial pain and numbness - curvature of the spine, or scoliosis How is syringomyelia diagnosed? 1. Your neurologist will first take your complete medical history. 2. A complete physical examination will be performed. 3. Tell your neurologist about your symptoms and how long you’ve had them. If your neurologist thinks you may have syringomyelia they will order an MRI scan to look for a syrinx in your spinal cord. An MRI scan is the most reliable diagnostic tool for syringomyelia. How is syringomyelia treated? Treatment depends on the progression of the disorder and whether you’re experiencing symptoms that disrupt your life. If you have no symptoms or mild symptoms, you may not need treatment. Your neurologist will monitor the progression of the disorder. EXTRA: Joanna David is a british actress who was diagnosed with Arnold - Chiari malformation and underwent brain surgery in 1993 to correct this malformation. ADVICE: Don't google your symptoms folks but always go visit your doctor!

