

💥𝐊𝐞𝐲 𝐩𝐨𝐢𝐧𝐭𝐬 & 𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐦𝐬 𝐨𝐟 𝐧𝐞𝐮𝐫𝐨𝐧💥 𝐊𝐞𝐲 𝐩𝐨𝐢𝐧𝐭𝐬:
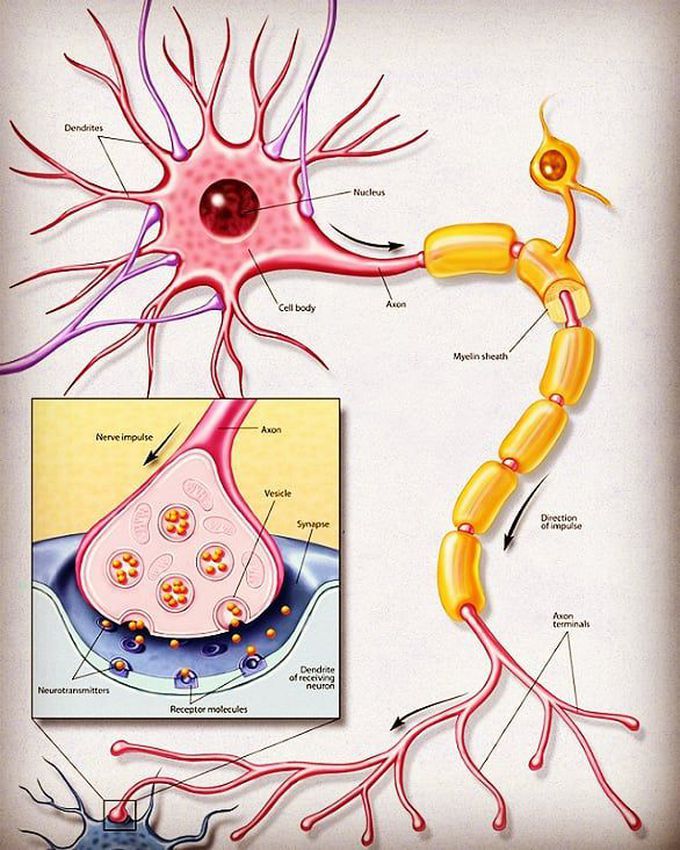
Neurons are specialized cells that transmit chemical and electrical signals in the brain; they are the basic building blocks of the central nervous system. The primary components of the neuron are the soma (cell body), the axon (a long slender projection that conducts electrical impulses away from the cell body), dendrites (tree-like structures that receive messages from other neurons), and synapses (specialized junctions between neurons). Some axons are covered with myelin, a fatty material that acts as an insulator and conductor to speed up the process of communication. Sensory neurons are neurons responsible for converting external stimuli from the environment into corresponding internal stimuli. Motor neurons are neurons located in the central nervous system (CNS); they project their axons outside of the CNS to directly or indirectly control muscles. Interneurons act as the “middle men” between sensory and motor neurons, which convert external stimuli to internal stimuli and control muscle movement, respectively. 𝐊𝐞𝐲 𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐦𝐬: Glial cell: Non-neuronal cells that provide structure and support to neurons. Synapse: The junction between the terminal of a neuron and either another neuron or a muscle or gland cell, over which nerve impulses pass. Myelin: A white, fatty material composed of lipids and lipoproteins that surrounds the axons of nerves and facilitates swift communication. Nodes of Ranvier: Periodic gaps in the myelin sheath where the signal is recharged as it moves along the axon
Source: https://www.instagram.com/p/BrXA3cShtre/?utm_source=ig_share_sheet&igshid=feb1bqslfh9lBreastfeeding and Medications IIDandy Walker Malformation | Diagnosis symptoms and treatment2-Minute Neuroscience: Brain AneurysmsSeizures (Epilepsy) Nursing NCLEX: Tonic-Clonic, Generalized, Focal, SymptomsStroke: Causes, Risk Factors, Treatment, and Prevention | Mass General BrighamEffects of sugar on teethNeurofibromatosisAbsence seizuresSymptoms of absence seizures

