

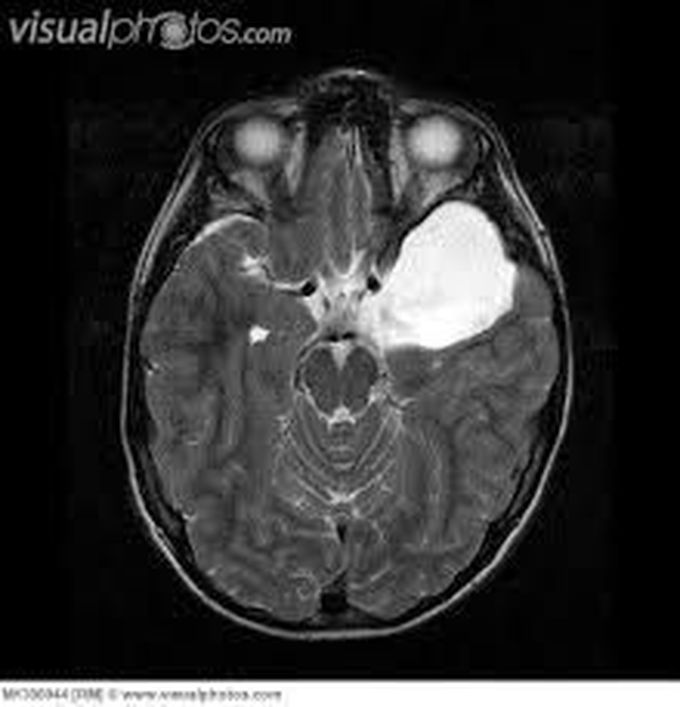
Arachnoid Cyst
Arachnoid cysts are cerebrospinal fluidcovered by arachnoidal cells and collagen that may develop between the surface of the brain and the cranial base or on the arachnoid membrane, one of the three meningeal layersthat cover the brain and the spinal cord.Arachnoid cysts are a congenital disorder and most cases begin during infancy; however, onset may be delayed until adolescence. Arachnoid cysts may also be classified as primary (congenital) or secondary (acquired) Signs and Symptoms ------------------------------------- Patients with arachnoid cysts may never show symptoms, even in some cases where the cyst is large. Therefore, while the presence of symptoms may provoke further clinical investigation Symptoms vary by the size and location of the cyst(s), though small cysts usually have no symptoms and are discovered only incidentally. On the other hand, a number of symptoms may result from large cysts CAUSES ------------------------ The exact cause of arachnoid cysts is not known. Researchers believe that most cases of arachnoid cysts are developmental malformations that arise from the unexplained splitting or tearing of the arachnoid membrane. Diagnosis --------------------- Diagnosis is principally by MRI Treatment -------------------- Most arachnoid cysts are asymptomatic and do not require treatment. Treatment may be necessary when symptomatic.A variety of procedures may be used to decompress (remove pressure from) the cyst. Surgical placement of a cerebral shunt: *An internal shunt drains into the subdural compartment. *A cystoperitoneal shunt drains to the peritoneal cavity. *Fenestration:Craniotomy with excision *Pharmacological treatments may address specific symptoms such as seizures or pain.

