

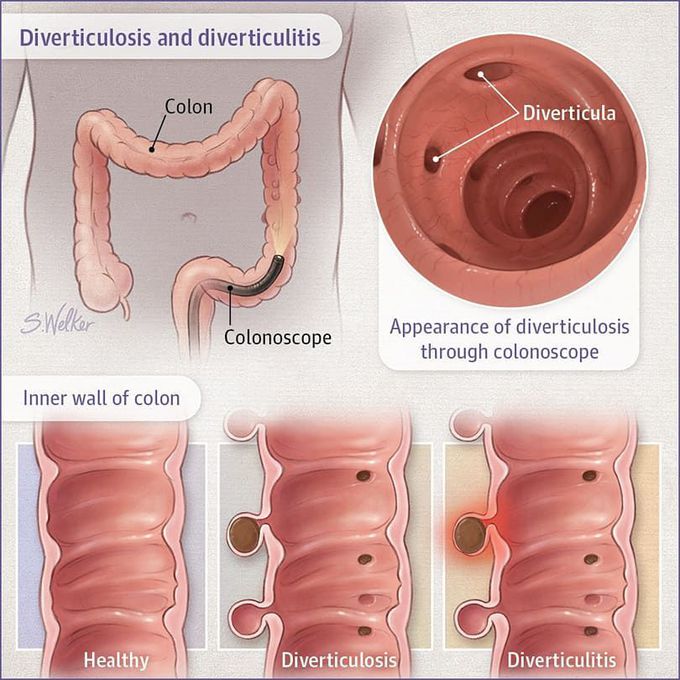
Diverticulosis
Diverticulosis is a condition in which small pouches (called diverticula) form at weak spots in the wall of the colon. Diverticulosis is common in older adults, occurring in about half of people between 60 and 80 years old. It affects men and women equally. Scientists do not know what causes diverticulosis. A low-fiber diet may play a role in developing the disease. Another cause might be abnormal contraction and spasm of the muscles in the colon wall. Obesity, lack of exercise, and some medications have been associated with diverticulosis. Symptoms Most people who have diverticulosis do not have any symptoms. When diverticulosis causes symptoms, it is called diverticular disease. Symptoms can include constipation, cramps, bloating, and painless bleeding from the rectum. Diverticular disease also includes diverticulitis. Diverticulitis occurs when diverticula become inflamed or infected. Symptoms include abdominal pain (usually on the left side), fever, nausea, vomiting, cramps, and constipation. Possible complications include Abscess Stricture (narrowing of part of the colon) Perforation (tear) Peritonitis (abdominal inflammation that can occur after a perforation) Fistula (abnormal connection between the colon and the bladder, small intestine, vagina, or skin) Diagnosis Because it does not usually cause symptoms, diverticulosis is often found when a test such as a colonoscopy is done for an unrelated reason. Diverticulosis and diverticular disease can also be diagnosed with a barium enema (x-ray scan). Diverticulitis is usually diagnosed with a computed tomography scan of the abdomen.
Source: https://www.instagram.com/p/BqUZAa8hHaq/?utm_source=ig_share_sheet&igshid=20kzkm8f78ki
