

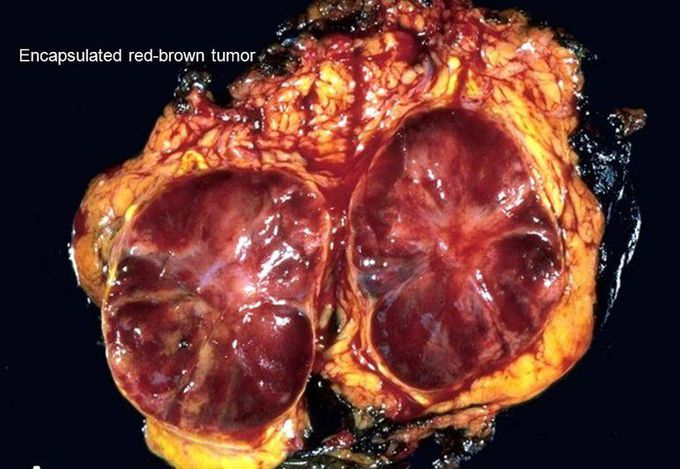
PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA (PCC)
A rare usually noncancerous (benign) tumor that develops in an adrenal gland. Usually, this type of tumor affects one of your two adrenal glands, but it can affect both. If you have a pheochromocytoma, the tumor releases hormones that cause either episodic or persistent high blood pressure. Untreated, a pheochromocytoma can result in severe or life-threatening damage to other body systems, especially the cardiovascular system. Most people with a pheochromocytoma are between the ages of 20 and 50, but the tumor can develop at any age. Surgical treatment to remove a pheochromocytoma usually returns blood pressure to normal. Symptoms Signs and symptoms of pheochromocytomas often include: High blood pressure Heavy sweating Headache Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia) Tremors Paleness in the face (pallor) Shortness of breath (dyspnea)

