

Zunaira salehabout 1 year ago
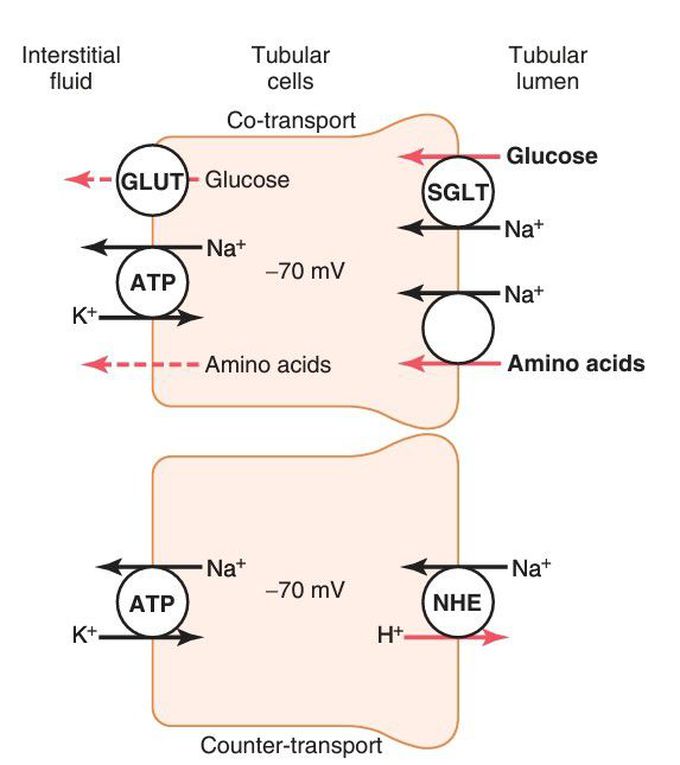
Mechanisms of secondary active transport.
The upper cell shows the co-transport of glucose and amino acids along with sodium ions through the apical side of the tubular epithelial cells, followed by facilitated diffusion through the basolateral membranes. The lower cell shows the counter-transport of hydrogen ions from the interior of the cell across the apical membrane and into the tubular lumen; movement of sodium ions into the cell, down an electrochemical gradient established by the sodium-potassium pump on the basolateral membrane, provides the energy for transport of the hydrogen ions from inside the cell into the tubular lumen. ATP, adenosine triphosphate; GLUT, glucose transporter; NHE, sodium- hydrogen exchanger; SGLT, sodium-glucose co-transporter.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

