

Sheeza Basharat8 months ago
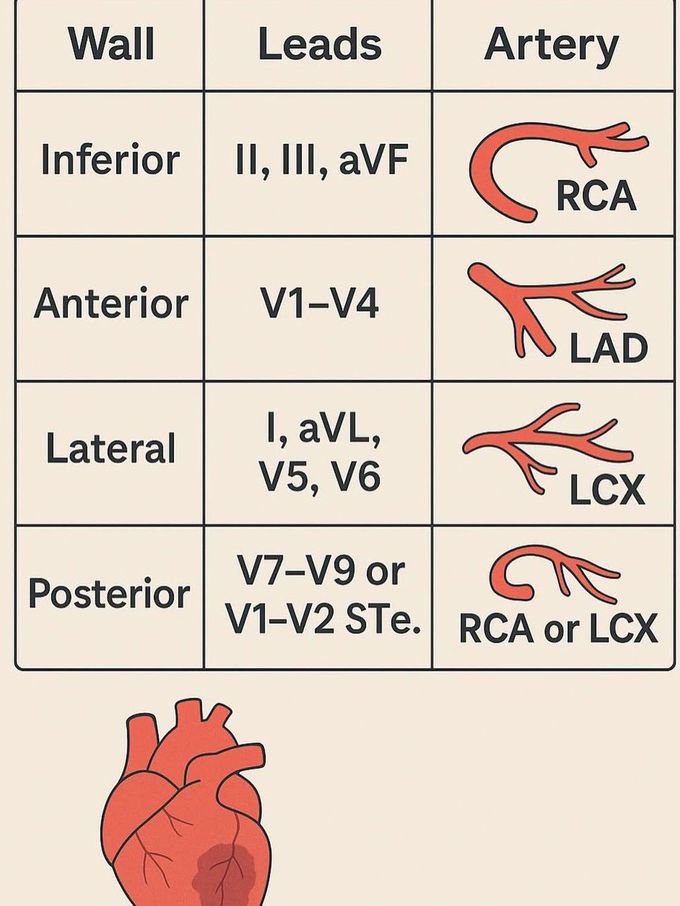
Localizing Myocardial Infarction
Myocardial infarction (MI) or heart attack, is localized based on the specific area of the heart muscle deprived of blood flow and oxygen, typically due to a blockage in a coronary artery. The location of the MI is determined using the 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG), which reveals characteristic changes in ST segments and Q waves, and by analyzing the patient's symptoms, such as chest pain, and other diagnostic tests like blood tests and echocardiograms.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!
Related posts
Trigeminal NerveChickenpox Vs MeaslesCord ProlapseKey Aspects of Cord ProlapseCord Prolapse- TypesThe Nucleus GigantocellularisFurosemide Dosing ProtocolPeripartum CardiomyopathyBitechchain Review - Is Bitechchain Scam Or legit?Prestigio Marketdex Review - Can Beginners Profit With Prestigio Marketdex? Expert Insights

