

Hunainabout 1 year ago
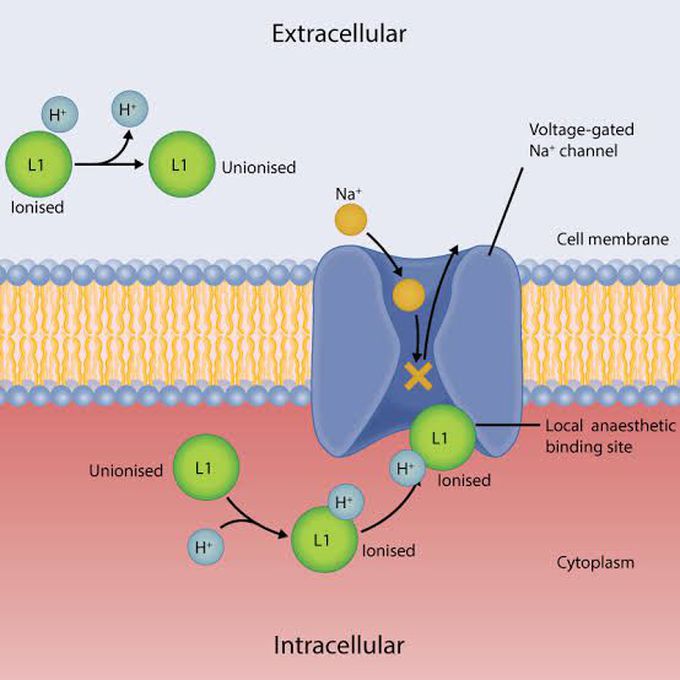
Mechanism of action of local anesthesia
Local anesthetics (LAs) work by blocking nerve impulses in the peripheral and central nervous systems. LAs bind to voltage-gated sodium channels in the nerve membrane, preventing sodium ions from entering the cell. This prevents the nerve cell membrane from depolarizing, and therefore prevents nerve impulses from propagating.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

