

Zunaira salehabout 1 year ago
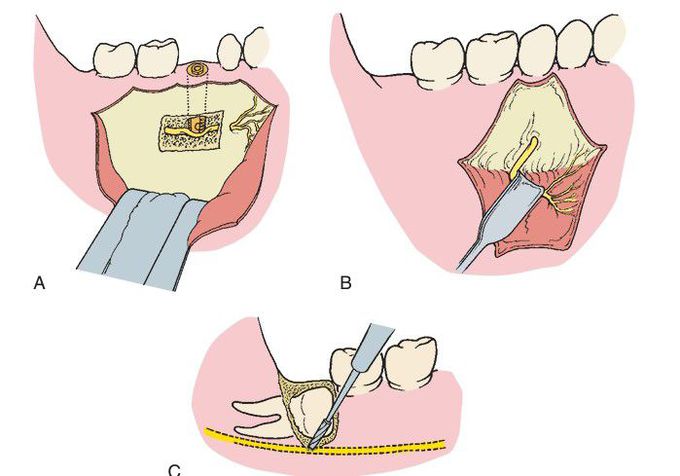
Three types of peripheral nerve injury.
(A) Neurapraxia. Injury to the nerve causes no loss of continuity of the axon or the endoneurium. The example shown is an implant placed in the inferior alveolar canal, compressing the nerve. (B) Axonotmesis. Injury to the nerve causes loss of axonal continuity but preserves the endoneurium. The example shown is overly aggressive retraction of mental nerve. (C) Neurotmesis. Injury to the nerve causes loss of axonal and endoneurium continuity. The example shows cutting of the inferior alveolar nerve during the removal of a deeply impacted third molar.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!
Related posts

