

Zunaira salehabout 1 year ago
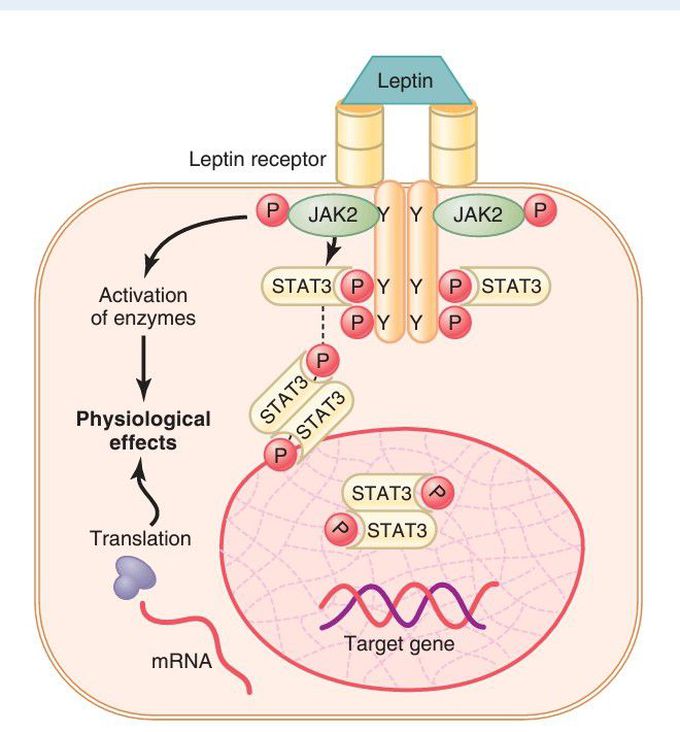
An enzyme-linked receptor—the leptin receptor.
The receptor exists as a homodimer (two identical parts), and leptin binds to the extracellular part of the receptor, causing phosphorylation (P) and activation of the intracellular associated janus kinase 2 (JAK2). This mechanism causes phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) proteins, which then activates the transcription of target genes and the synthesis of proteins. JAK2 phosphorylation also activates several other enzyme systems that mediate some of the more rapid effects of leptin. Y, specific tyrosine phosphorylation sites.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!
Related posts
Sensory Receptors -IICholinergic ReceptorsSensory TransductionAdrenergic ReceptorsSensory Receptors -IProlactin physiology- AnimationSignalling of intra cellular receptors-
MechanismEffect of calcium on cardiac cells: excitation contraction couplingReceptorsMechanism of activation of a G protein–coupled receptor.

