

Zunaira salehabout 1 year ago
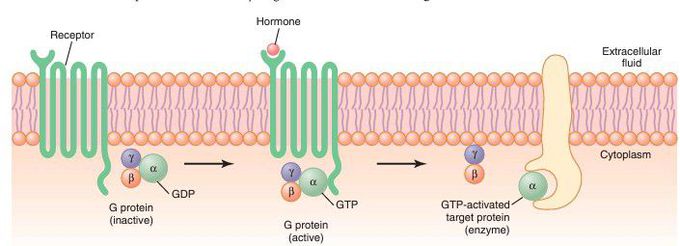
Mechanism of activation of a G protein–coupled receptor.
When the hormone activates the receptor, the inactive α, β, and γ G protein complex associates with the receptor and is activated, with an exchange of guanosine triphosphate (GTP) for guanosine diphosphate (GDP). This process causes the α subunit (to which the GTP is bound) to dissociate from the β and γ subunits of the G protein and to interact with membrane-bound target proteins (enzymes) that initiate intracellular signals.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

