

Zunaira salehabout 1 year ago
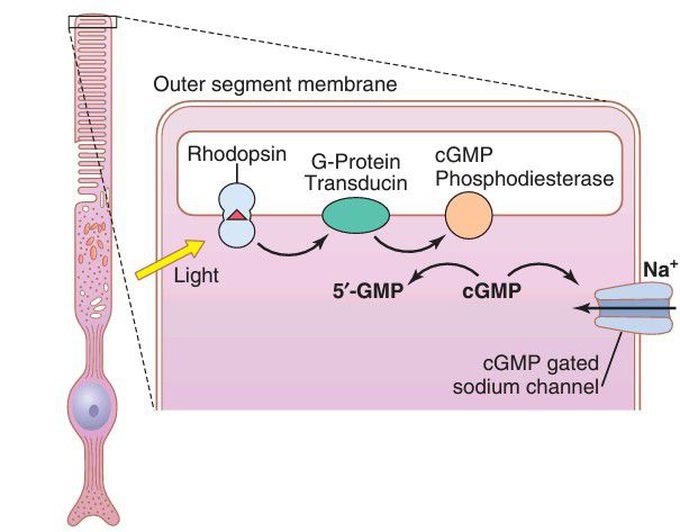
Phototransduction
Phototransduction in the outer segment of the photoreceptor (rod or cone) membrane. When light hits the photoreceptor (e.g., a rod cell), the light-absorbing retinal portion of rhodopsin is activated. This activation stimulates transducin, a G protein, which then activates cGMP phosphodiesterase. This enzyme catalyzes the degradation of cGMP into 5′-GMP. The reduction in cGMP then causes closure of the sodium channels, which, in turn, causes hyperpolarization of the photoreceptor.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

