

Zunaira salehabout 1 year ago
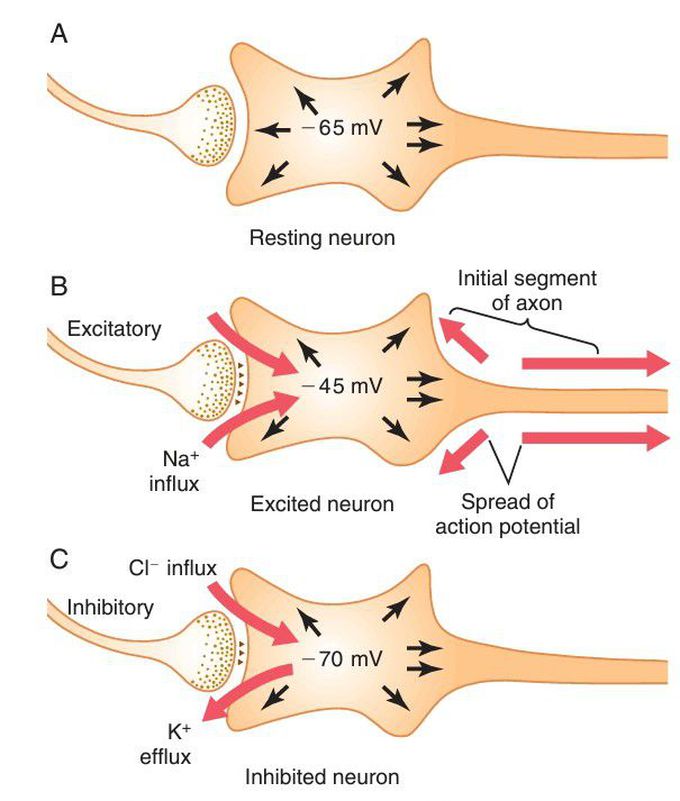
Three states of a neuron
A, Resting neuron, with a normal intraneuronal potential of −65 millivolts. B, Neuron in an excited state, with a less negative intraneuronal potential (−45 millivolts) caused by sodium influx. C, Neuron in an inhibited state, with a more negative intraneuronal membrane potential (−70 millivolts) caused by potassium ion efflux, chloride ion influx, or both.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

