

Zunaira salehabout 1 year ago
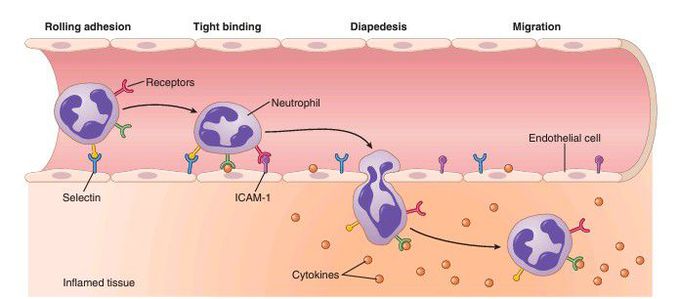
Migration of neutrophils from the blood into inflamed tissue.
Cytokines and other biochemical products of the inflamed tissue cause increased expression of selectins and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in the surface of endothelial cells. These adhesion molecules bind to complementary molecules/receptors on the neutrophil, causing it to adhere to the wall of the capillary or venule. The neutrophil then migrates through the vessel wall by diapedesis toward the site of tissue injury.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

