

Zunaira salehabout 1 year ago
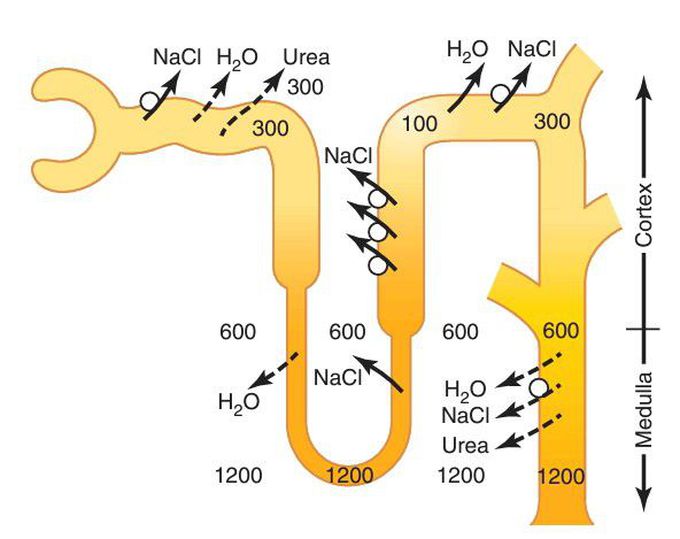
Formation of concentrated urine
Formation of a concentrated urine when antidiuretic hormone (ADH) levels are high. Note that the fluid leaving the loop of Henle is dilute but becomes concentrated as water is absorbed from the distal tubules and collecting tubules. With high ADH levels, the osmolarity of the urine is about the same as the osmolarity of the renal medullary interstitial fluid in the papilla, which is about 1200 mOsm/L. (Numerical values are in milliosmoles per lite
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

