

Zunaira salehabout 1 year ago
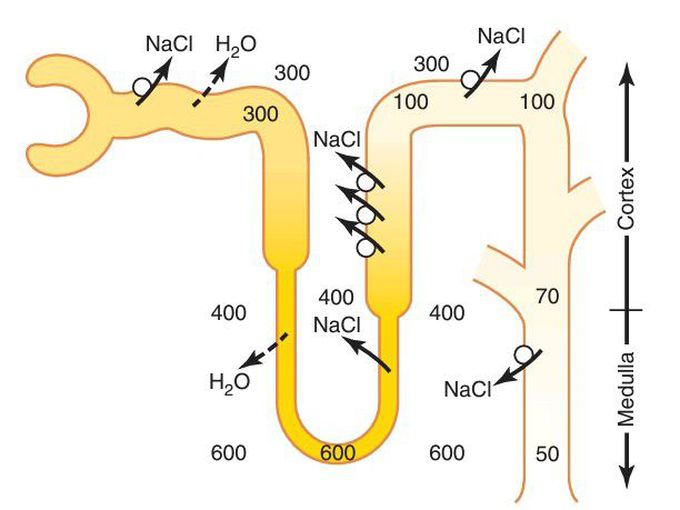
Dilute and concentrated urine
Formation of dilute urine when antidiuretic hormone (ADH) levels are very low. Note that in the ascending loop of Henle, the tubular fluid becomes very dilute. In the distal tubules and collecting tubules, the tubular fluid is further diluted by the reabsorption of sodium chloride and the failure to reabsorb water when ADH levels are very low. The failure to reabsorb water and continued reabsorption of solutes lead to a large volume of dilute urine. (Numerical values are in milliosmoles per liter.)
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

