

Zunaira salehover 1 year ago
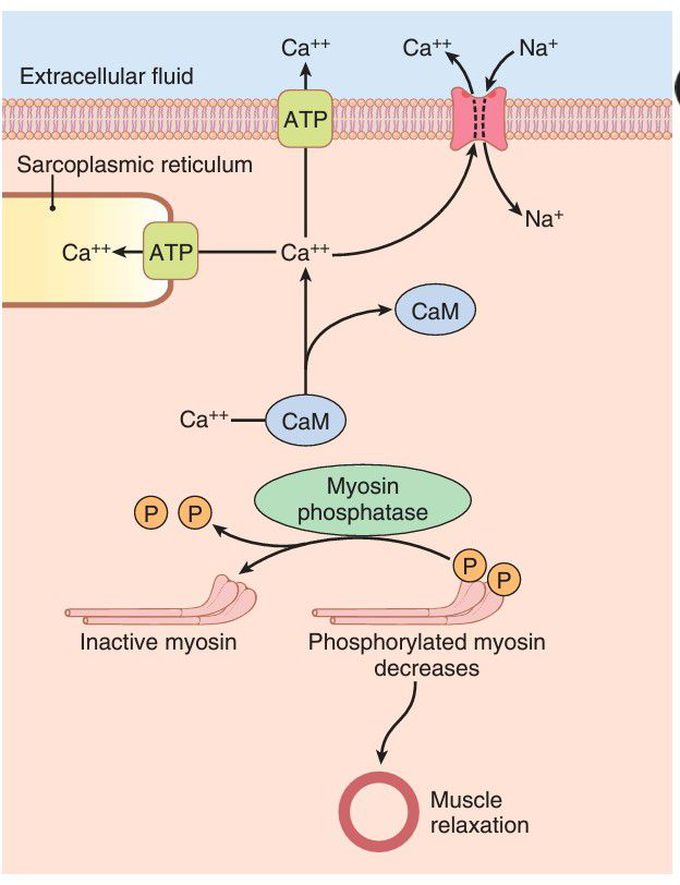
Relaxation of smooth muscle
Relaxation of smooth muscle occurs when calcium ion (Ca++) concentration decreases below a critical level as Ca++ is pumped out of the cell or into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Ca++ is then released from calmodulin (CaM) and myosin phosphatase removes phosphate from the myosin light chain, causing detachment of the myosin head from the actin filament and relaxation of the smooth muscle. ADP, adenosine diphosphate; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; Na+, sodium; P, phosphate.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

