

Zunaira salehover 1 year ago
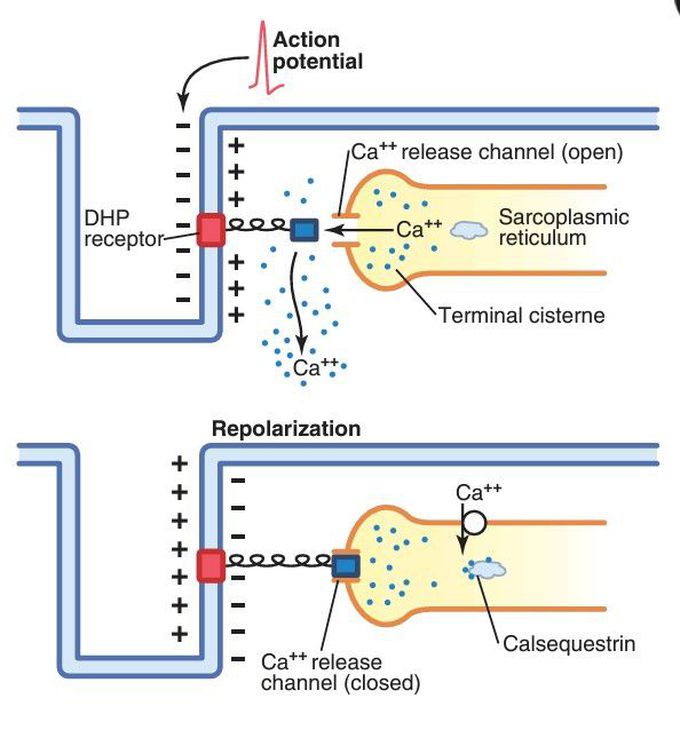
Excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle.
The top panel shows an action potential in the transverse tubule that causes a conformational change in the voltage-sensing dihydropyridine (DHP) receptors, opening the Ca++ release channels in the terminal cisternae of the sarcoplasmic reticulum and permitting Ca++ to rapidly diffuse into the sarcoplasm and initiate muscle contraction. During repolarization (bottom panel), the conformational change in the DHP receptor closes the Ca++ release channels and Ca++ is transported from the sarcoplasm into the sarcoplasmic reticulum by an adenosine triphosphate–dependent calcium pump.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

