

Zunaira salehover 1 year ago
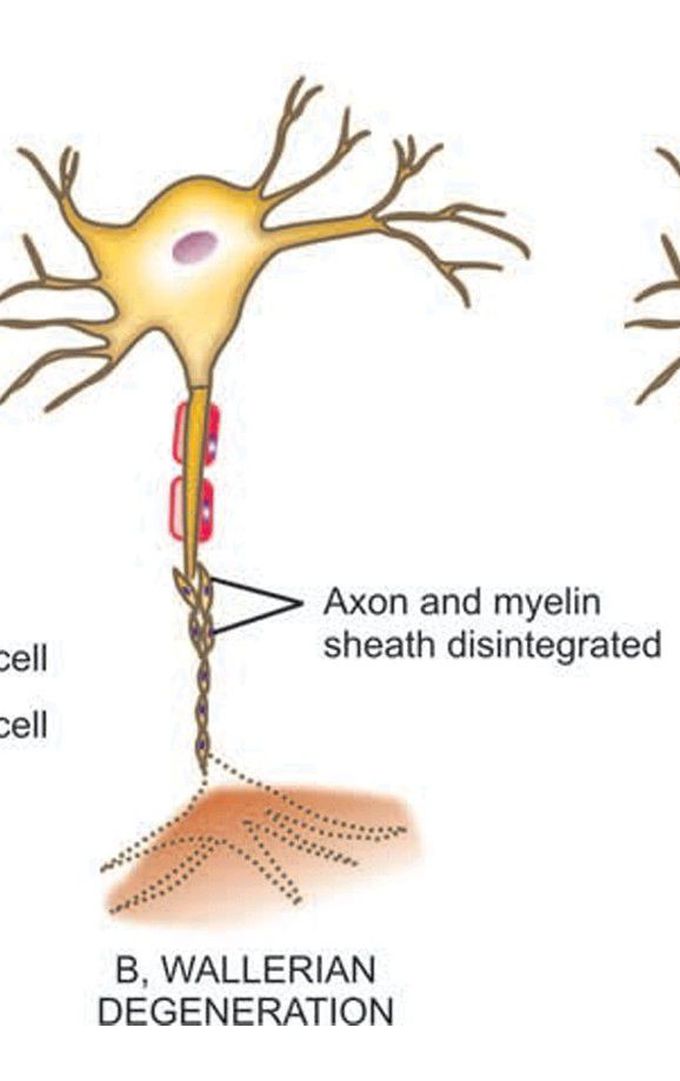
Pathologic reaction of peripheral nerve injury (1)
Wallerian degeneration occurs after transection of the axon which may be as a result of knife wounds, compression, traction and ischaemia. Following transection, initially there is accumulation of organelles in the proximal and distal ends of the transection sites. Subsequently, the axon and myelin sheath distal to the transection site undergo disintegration upto the next node of Ranvier, followed by phagocytosis. The process of regeneration occurs by sprouting of axons and proliferation of Schwann cells from the proximal end.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

