

Zunaira salehover 1 year ago
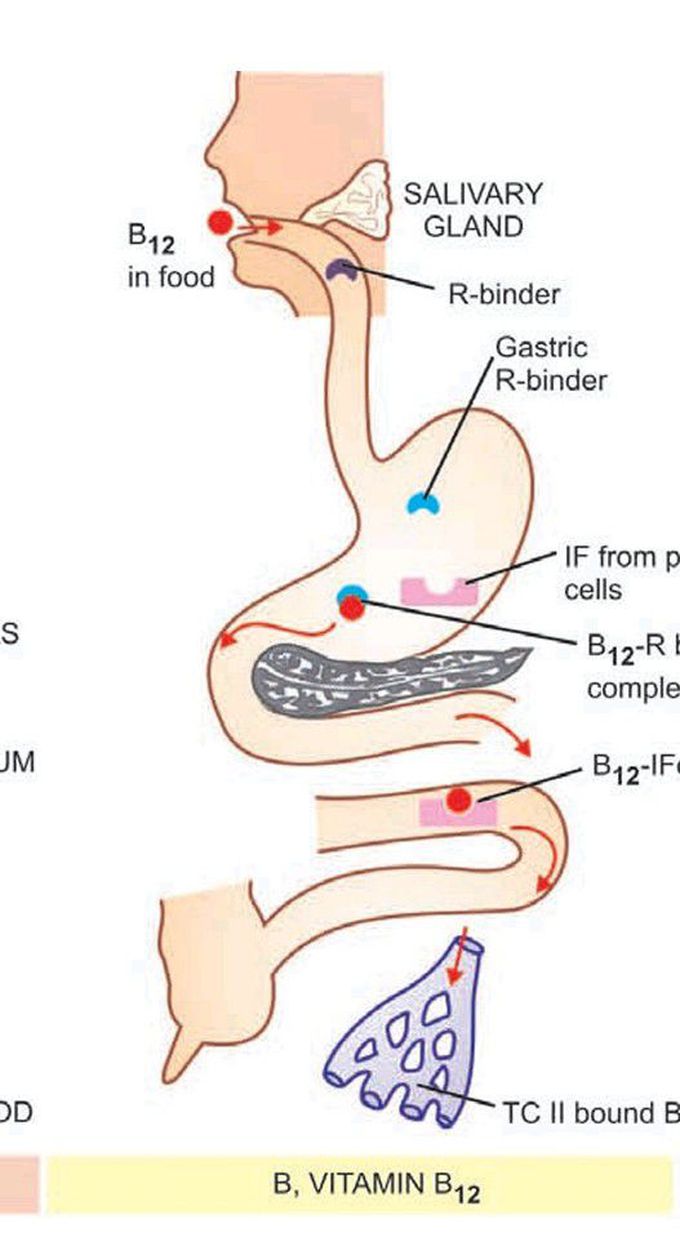
Vitamin B12 absorption and transport
Vitamin B12 or cobalamin is a complex organometallic compound having a cobalt atom situated within a corrin ring, similar to the structure of porphyrin from which haem is formed. In humans, there are 2 metabolically active forms of cobalamin—methylcobalamin and adenosyl-cobalamin, which act as coenzymes. The therapeutic vitamin B12 preparation is called cyanocobalamin.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

