

Zunaira salehover 1 year ago
Pulmonary oedema
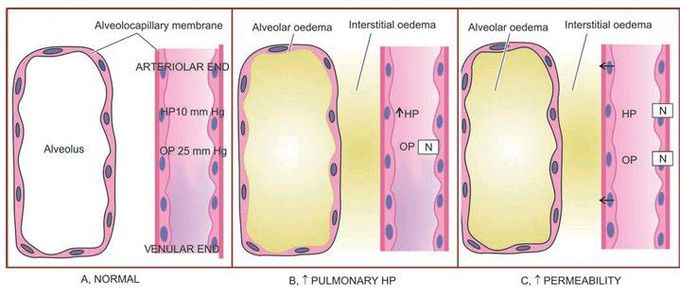
Mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of pulmonary oedema. A, Normal fluid exchange at the alveolocapillary membrane (capillary endothelium and alveolar epithelium). B, Pulmonary oedema via elevated pulmonary hydrostatic pressure. C, Pulmonary oedema via increased vascular permeability.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

