

Symptoms of stroke
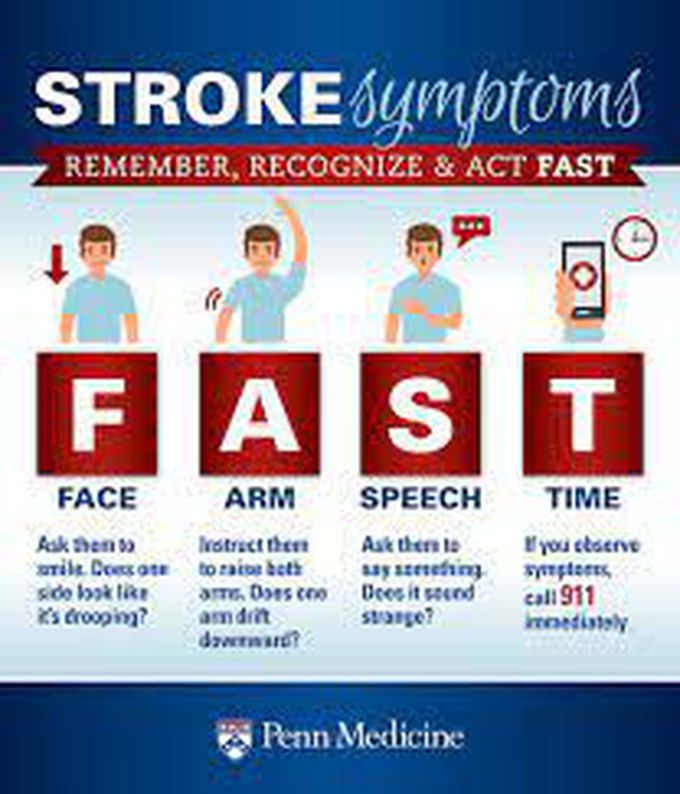
The symptoms of a stroke often appear without warning. Some of the main symptoms include: confusion, including difficulty speaking and understanding speech a headache, possibly with altered consciousness or vomiting numbness or an inability to move parts of the face, arm, or leg, particularly on one side of the body vision problems in one or both eyes difficulty walking, including dizziness and a lack of coordination Stroke can lead to long-term health problems. Depending on the speed of the diagnosis and treatment, a person can experience temporary or permanent disabilities after a stroke. Some people may also experience: bladder or bowel control problems depression paralysis or weakness on one or both sides of the body difficulty controlling or expressing their emotions Symptoms vary and may range in severity. Learning the acronym “FAST” is a good way to remember the symptoms of stroke. This can help a person seek prompt treatment. FAST stands for: Face drooping: If the person tries to smile, does one side of their face droop? Arm weakness: If the person tries to raise both their arms, does one arm drift downward? Speech difficulty: If the person tries to repeat a simple phrase, is their speech slurred or unusual? Time to act: If any of these symptoms are occurring, contact the emergency services immediately.

