

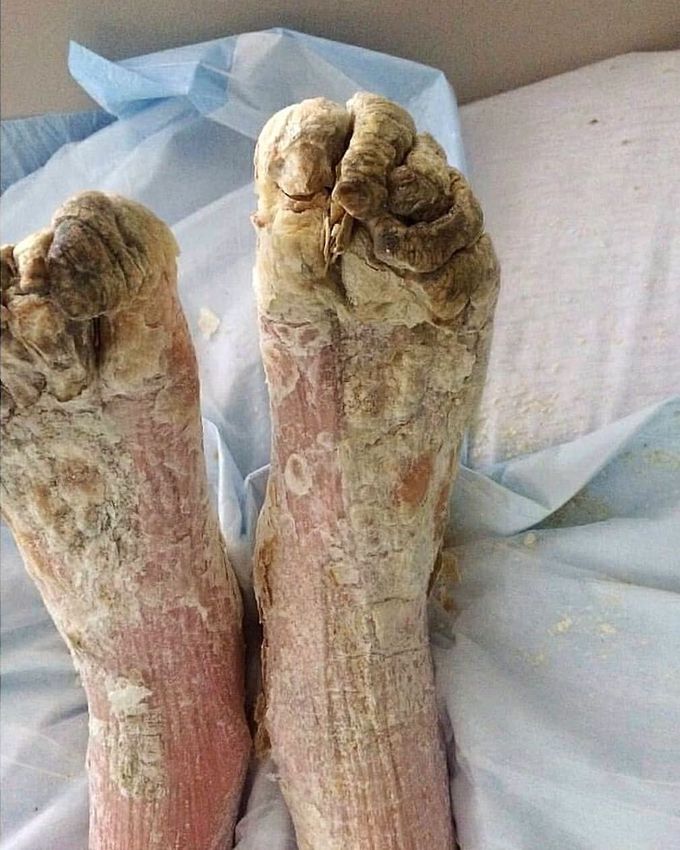
A rare form of crusted scabies (also called Norwegian scabies)!!
This is a peculiar and severe version of scabies showing hyperkeratotic or psoriasiform papules or plaques or sometimes diffuse erythroderma. It is caused by a common scabies mite, which often develops in people with weakened immunity. The most susceptible are people whose immunity has been reduced due to AIDS, tuberculosis, lupus erythematosus, etc. Also, patients with a neurological disease, the elderly, the disabled, or those who are mentally impaired. The clinical feature of the Norwegian scabies is a massive layering of crusts on different areas of the skin. The peels of a yellowish-dirty, brownish-black color, dense, with a smooth or striated surface with a thickness of several millimeters to 2-3 cm are arranged in several layers (5-7). Between these layers and under the whole crust a large number of scabies mites are found. The usual features of scabies (itching and a rash) may be absent. Crusted scabies is very contagious and can spread easily both by direct skin-to-skin contacts and through contaminated items such as clothing, bedding, and furniture. It is caused by superinfestation with Sarcoptes scabiei var hominis, but why the crusted scabies develops is unknown. People with crusted scabies should receive quick and aggressive medical treatment for their infestation to prevent outbreaks of scabies. Ivermectin is used for treatment.
Living with Lupus is often a battle not just against the illness itself, but also against the emotional weight of uncertainty, fatigue, and the toll of long-term medications. For one courageous woman, that battle began in 2013. Diagnosed after Lupus had already affected her joints and internal organs, she was quickly placed on medication that initially helped. But as time went on, her health declined again this time with more frequent flare-ups and increasingly difficult side effects. Like many others with chronic illness, she faced the crushing weight of hopelessness. Each day became harder than the last, and conventional treatments no longer offered the comfort they once did. But in March 2020, at her lowest point, she made a decision that changed everything.Out of desperation and with a healthy dose of skepticism she turned to NaturePath Herbal Clinic, hoping their natural Lupus treatment might offer at least some relief. What happened next went far beyond her expectations.After completing a six-month herbal program, her flare-ups stopped entirely. Her energy returned. The chronic pain that had defined her daily life began to fade. For the first time in years, she felt like herself again. Not just alive but truly living.Her story is not just one of healing; it’s one of resilience, open-mindedness, and the courage to try something new when all else fails. By sharing her journey, she hopes to offer something priceless to others living with Lupus: hope.This treatment has been a true breakthrough for her. If you’re searching for a safe, natural, and effective alternative, I genuinely recommend giving this a chance.”www.naturepathherbalclinic.com or email them at info@naturepathherbalclinic.com
Hemodynamic stimuli&nonhemodynamic stimuliEffects of sugar on teeth


