

Vijay Kumarabout 2 years ago
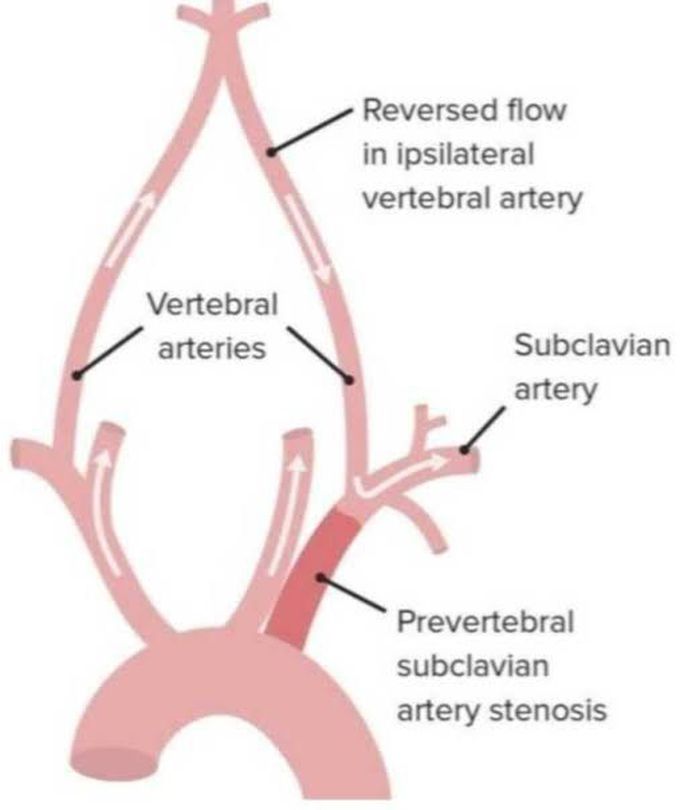
Subclavian Steal Syndrome
Subclavian steal syndrome (SSS), also known as subclavian-vertebral artery steal syndrome, is a phenomenon causing retrograde flow in an ipsilateral vertebral artery due to stenosis or occlusion of the subclavian artery, proximal to the origin of the vertebral artery. Subclavian steal is asymptomatic in most patients and does not warrant invasive evaluation or treatment. It can manifest in some patients with symptoms of arterial insufficiency affecting the brain or the upper extremity, supplied by the subclavian artery.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

