

Pyemotes ventricosus Dermatitis
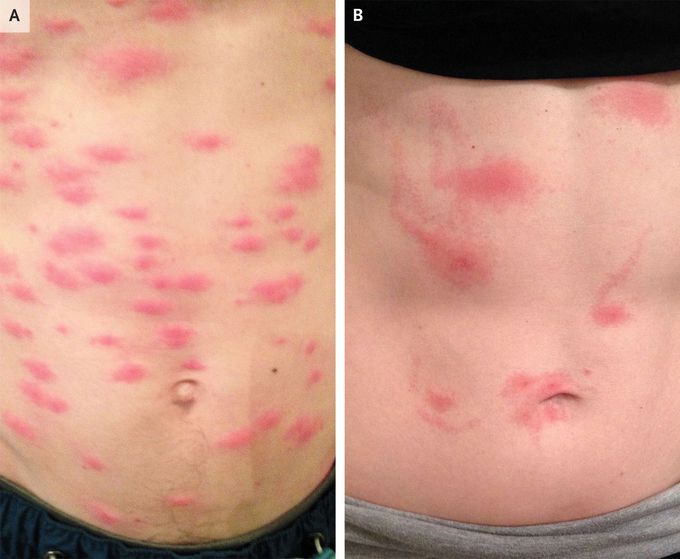
A 30-year-old man and a 30-year-old woman presented to the infectious disease clinic with a 3-day history of itchy skin lesions. They reported no history of outdoor activities. On physical examination, the man had pruritic papules across his trunk and abdomen (Panel A). On the woman’s abdomen, there were several erythematous macules, some of which had central dots and serpiginous tracts emanating from them that gave the appearance of a comet (Panel B). Owing to concern about a household infestation, the couple’s furniture was examined. Common furniture beetles — also known as Anobium punctatum, a type of wood-boring beetle — were identified. With the knowledge that common furniture beetles can be parasitized by the microscopic mite Pyemotes ventricosus, also known as the European straw itch mite, a clinical diagnosis of P. ventricosus dermatitis was made. In this condition, skin lesions develop within 24 hours after the receipt of painless mite bites and may manifest with a comet shape, as was seen in this case. The couple’s infested furniture was removed. Treatment with topical glucocorticoids and antihistamines was given, and the skin lesions resolved in 8 days.

