

Vijay Kumarover 2 years ago
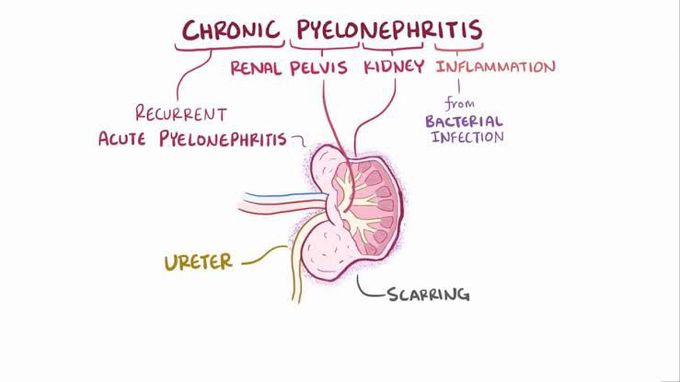
Chronic pyelonephritis
Chronic pyelonephritis is characterized by inflammation and scarring induced by recurrent or persistent kidney infection, vesicoureteral reflux, or other causes of urinary tract obstruction. It occurs almost exclusively in patients with major anatomic anomalies, most commonly young children with vesicoureteral reflux (VUR). The diagnosis of chronic pyelonephritis is made on the basis of imaging studies such as ultrasound or CT scanning. Treatment options include prophylactic antibiotics, endoscopic injection of dextranomer hyaluronic acid, and antireflux surgery. [4] Selecting the treatment option for different grades of VUR reflux depends on the clinical presentation and renal function.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

