

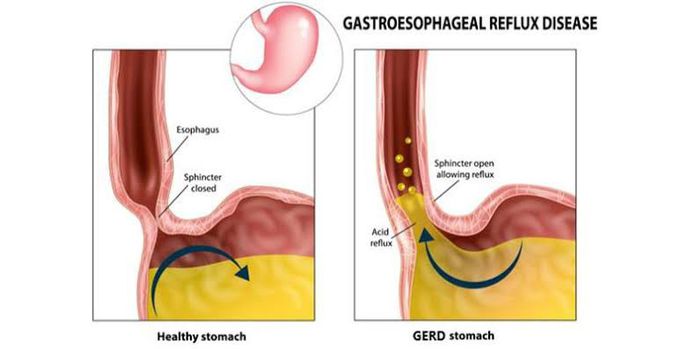
Gastro-esophageal Reflux Disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease occurs when the amount of gastric juice that refluxes into the esophagus exceeds the normal limit, causing symptoms with or without associated esophageal mucosal injury. Typical esophageal symptoms include the following: Heartburn Regurgitation Dysphagia Abnormal reflux can cause atypical (extraesophageal) symptoms, such as the following: Coughing and/or wheezing Hoarseness, sore throat Otitis media Noncardiac chest pain Enamel erosion or other dental manifestations The following studies are used to evaluate patients with suspected gastroesophageal reflux disease: Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy/esophagogastroduodenoscopy: Mandatory Esophageal manometry: Mandatory Ambulatory 24-hour pH monitoring: Criterion standard in establishing a diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease

