

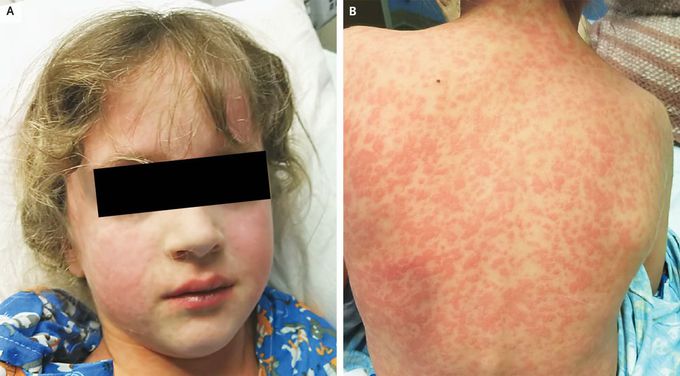
Amoxicillin Rash in Infectious Mononucleosis
A 7-year-old girl presented to the emergency department with an itchy rash. Eight days before presentation, she had been seen by her pediatrician for pharyngitis and received treatment with amoxicillin. At the current visit, her temperature was 39.8°C. Physical examination revealed generalized erythematous papules and macules involving her face (Panel A), her trunk (Panel B), and her arms and legs, sparing her palms and the soles of her feet. The tonsils were purulent, and the anterior and posterior cervical lymph nodes were enlarged. Laboratory studies showed a white-cell count of 8700 per cubic millimeter (reference range, 4000 to 11,500), with 66% lymphocytes (reference range, 20 to 40). A mononuclear spot test was positive. A diagnosis of amoxicillin rash in infectious mononucleosis was made. Patients who receive amoxicillin for the treatment of infectious mononucleosis consequent to infection with Epstein–Barr virus may be subject to the development of a morbilliform rash. However, this rash may not be predictive of a true allergy to penicillins. The patient’s parents were advised to stop the amoxicillin, and the patient’s rash resolved completely within 3 weeks.

