

Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
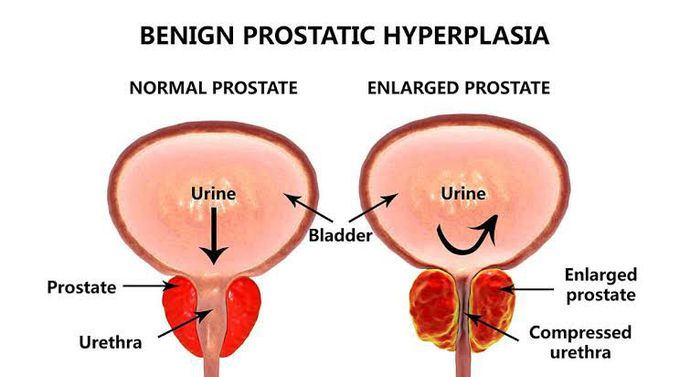
Benign prostatic hyperplasia—also called BPH—is a condition in men in which the prostate gland is enlarged and not cancerous. Benign prostatic hyperplasia is also called benign prostatic hypertrophy or benign prostatic obstruction.occurs mainly in older men. Men with the following factors are more likely to develop benign prostatic hyperplasia: -Age 40 years and older -Family history of benign prostatic hyperplasia medical conditions such as obesity, heart and circulatory disease, and type 2 diabetes -Lack of physical exercise -Erectile dysfunctional Lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia may include urinary frequency—urination eight or more times a day urinary urgency—the inability to delay urination trouble starting a urine stream a weak or an interrupted urine stream dribbling at the end of urination nocturia—frequent urination during periods of sleep urinary retention urinary incontinence—the accidental loss of urine pain after ejaculation or during urination urine that has an unusual color or smell.Treatment options for benign prostatic hyperplasia may include lifestyle changes medications (alpha blockers, phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors, 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, combination medications) minimally invasive procedures ( transurethral needle ablation, transurethral microwave thermotherapy, high-intensity focused ultrasound, transurethral electro-vaporization, water-induced thermotherapy, prostatic stent insertion) surgery

