

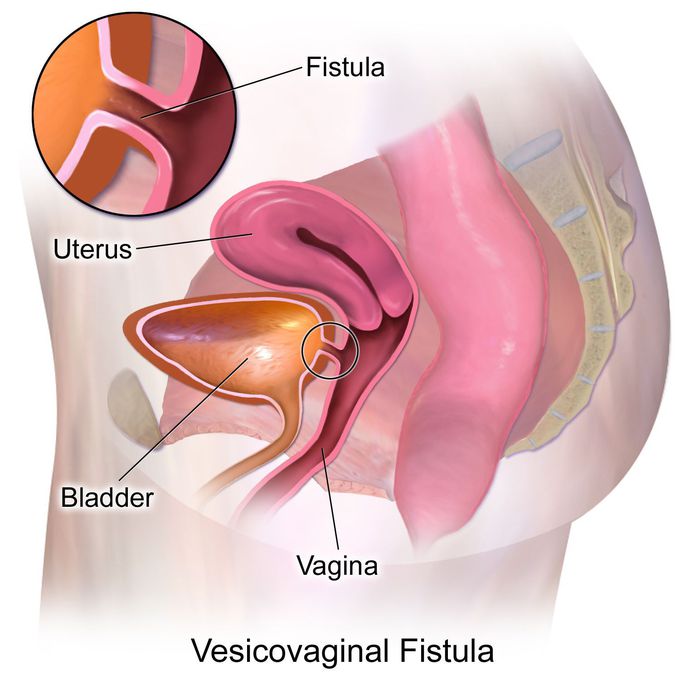
Vesicovaginal fistula
Vesicovaginal fistula (VVF) is a subtype of female urogenital fistula (UGF). VVF is an abnormal fistulous tract extending between the bladder and the vagina that allows the continuous involuntary discharge of urine into the vaginal vault.An accurate diagnosis is paramount before consideration of repair. A variety of methods are available to the clinician, and any excessive or suspicious vaginal discharge in a patient who recently underwent pelvic surgery or who has a history of pelvic radiotherapy should be evaluated promptly for a UGF.In developing countries, the predominant cause of VVF is prolonged obstructed labor (97%). VVFs are associated with marked pressure necrosis, edema, tissue sloughing, and cicatrization. The frequency of VVF is largely underreported in developing countries.

