

Cardiac Auscultation
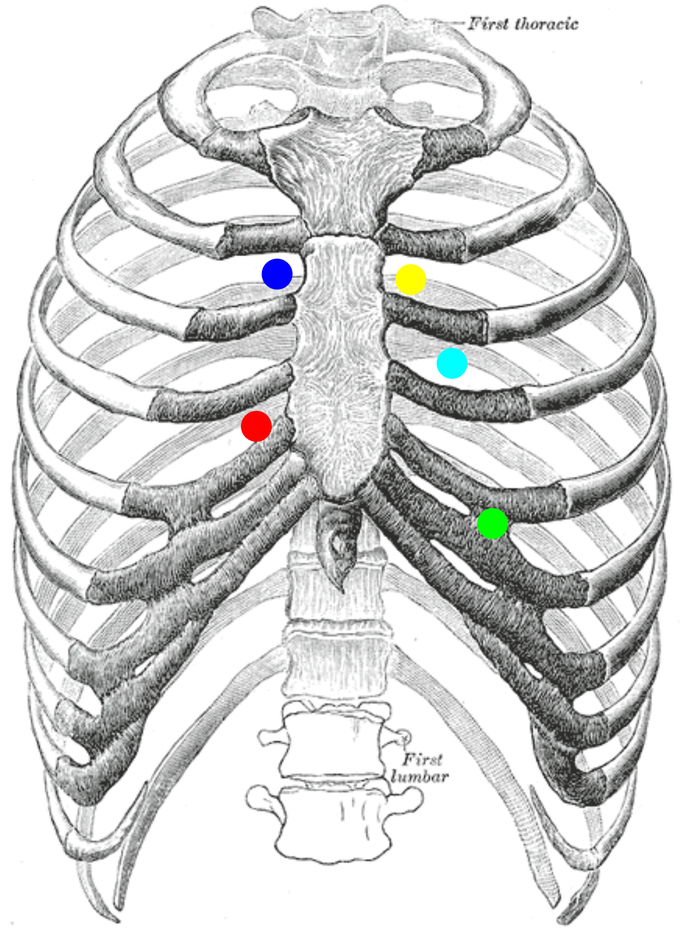
Auscultation of the heart is a fundamental practice during the objective examination, and it should be performed at very specific points that are named auscultation foci. There are 5 main foci and they go to identify the sound projections of the 4 heart valves (mitral, tricuspid, aortic semilunar, and pulmonary semilunar) plus a fifth area that is named the erb point. Aortic focus (DARK BLUE). It is present in the right II intercostal space on the marginal or parasternal line (it is important to auscultate this foci in the elderly subject because atherosclerotic pathology can easily affect this foci, giving rise to a murmur, whereas in an older hypertensive patient in this foci we can hear a jolting tone, an accentuated first tone) Pulmonary foci (YELLOW) Located on the left II intercostal space on the left marginosternal or parasternal line. Tricuspid foci (RED) Found on the right IV intercostal space at the margin of the sternum. Mitral foci (GREEN) It is located on the fourth to fifth intercostal space at the level of the left hemiclavicular line (represents the itctus of the tip of the heart). Erb's foci (BLUE). Representing the elective focus of aortic murmurs, it belongs to the mesocardium and is located in the center of the quadrilateral determined by the remaining four auscultation points. It is located at the level of the left third intercostal space on the parasternal line, immediately below the pulmonary artery foci. Some sources locate it at the level of the fourth intercostal space. It is the point at which auscultation of the aortic component of the second heart tone and heart murmurs caused by aortic valve alterations can be performed.

