

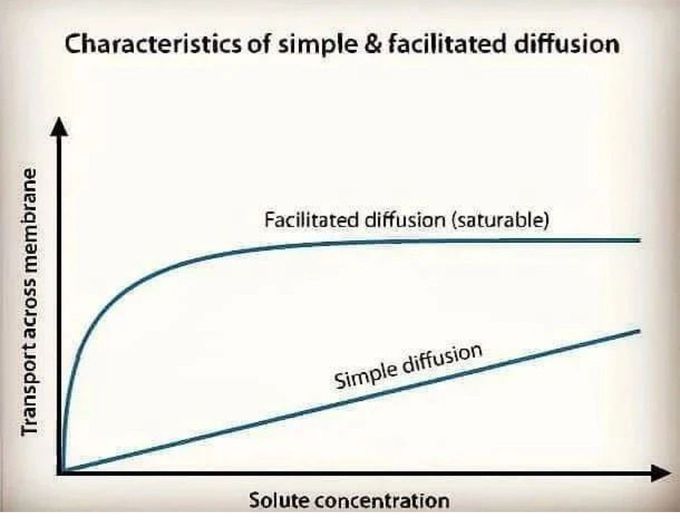
Diffusion
The image above illustrates the difference between the rate of transport of solute across the cell membrane in simple diffusion (line 2) and carrier-mediated transport(line 1). There are two types of diffusion: Simple diffsion - molecules move through a membrane without the help of carries proteins. Facilitated diffsion - requires carrier proteins. Carrier proteins are typ typically transmembrane proteins that possess binding sites for the substrate they transport. Binding is followed by movement of thesubstrate across the cell membrane to the intracellular space, where it is released into the cytoplasm. Because there is a definite number of carrier proteins in the cell membrane, transporter saturation occurs with facilitated diffsion, and can be seen as a flattening of the curve (maximum diffsion speed), even as solute concentrat on continues to increase. This maximum rate of transport is referred to as the transpor maximum (Tm) and is similar in principle to theVmax standard enzyme kinetics

