

Myocarditis
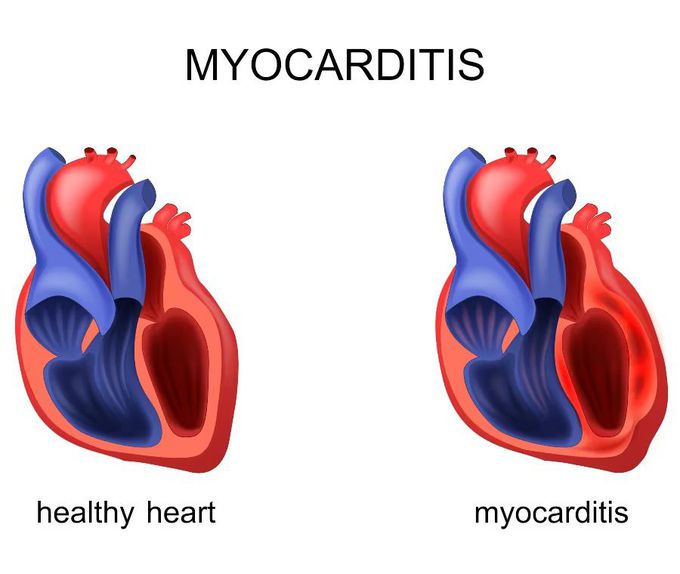
Myocarditis is a medical condition involving inflammation of the muscle tissue of the heart, known as the myocardium. This inflammation can damage the heart and affect its ability to effectively pump blood through the body. The causes of myocarditis can vary; it is often associated with viral infections, such as influenza virus, Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus. Other infections that can cause myocarditis include those caused by bacteria, fungi and parasites. However, it can also be caused by autoimmune diseases, allergic reactions to drugs or toxins, or be a complication of systemic diseases such as sarcoidosis. Symptoms of myocarditis can vary from mild to severe and may include fatigue, weakness, chest pain, dyspnoea (difficulty breathing), palpitations and swelling of the legs, ankles and feet. In some cases it may be asymptomatic and only be discovered during a routine medical examination or following complications such as heart failure or arrhythmias. The diagnosis of myocarditis can be complex, as the symptoms may be similar to other heart diseases. The physician may use a combination of examinations and tests, including electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram, blood tests to detect markers of inflammation, and endomyocardial biopsy (taking a tissue sample from the heart for analysis). The treatment of myocarditis depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the symptoms. In many cases, rest and taking anti-inflammatory drugs may be sufficient to manage the inflammation and relieve symptoms, while in more severe cases, heart medications, such as beta-blockers or diuretics, may be prescribed to improve heart function. In more extreme cases, hospitalisation and the use of advanced therapies such as ventricular assist devices or heart transplantation may be required. It is important to emphasise that myocarditis can have long-term consequences for heart health and in some cases lead to permanent damage to the myocardium and increase the risk of arrhythmias, heart failure and sudden death.

