
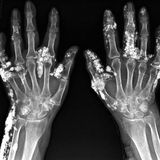
Normal plasma (left sample) and lipemic plasma (right two samples).
These are sample of hyperlipidemic blood in a vacutainer with EDTA left to settle for four hours without centrifugation, the lipids separated into the top fraction. Hyperlipidemia is abnormally elevated levels of any or all lipids or lipoproteins in the blood. These fats include cholesterol and triglycerides. You can control some of its causes, but not all of them. Hyperlipidemia is treatable, but it's often a life-long condition. Hyperlipidemias are divided into primary and secondary subtypes. Primary hyperlipidemia is usually due to genetic causes (such as a mutation in a receptor protein), while secondary hyperlipidemia arises due to other underlying causes such as diabetes. Lipid and lipoprotein abnormalities are common in the general population and are regarded as modifiable risk factors for cardiovascular disease due to their influence on atherosclerosis. In addition, some forms may predispose to acute pancreatitis. Atherosclerosis is the accumulation of lipids, cholesterol, calcium, fibrous plaques within the artery walls of the heart. This accumulation narrows the blood vessel and reduce blood flow and oxygen to muscles of the heart. Complete blockage of the artery causes infarction of the myocardial cells, known as heart attack or myocardial infarction. The buildup can also cause a blood clot to form. If a blood clot breaks off and travels to the heart, it causes a heart attack. If it goes to the brain, it can cause a stroke. source: IGmedicalpedia
These tubes do not contain EDTA. They are serum separater tubes, which separated the serum from the whole blood after centrafugation.

