

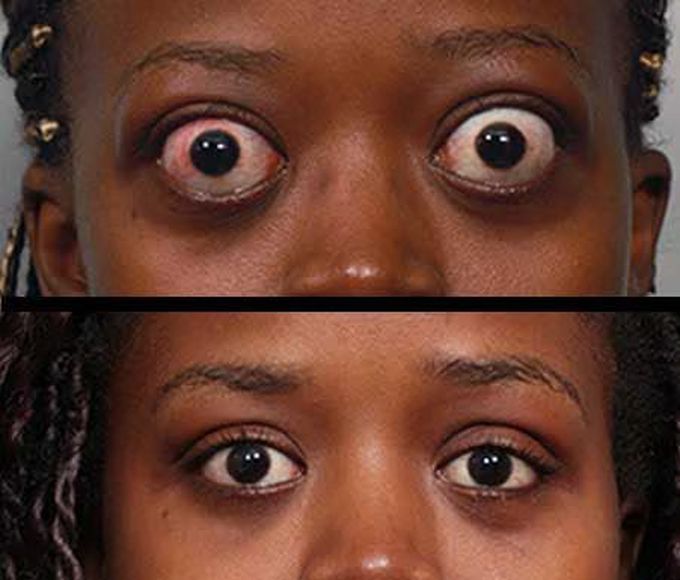
Basedow ophthalmopathy
Basedowian ophthalmopathy is a term used to describe an eye disease resulting from an alteration in the functioning of one of the most important glands of our body, the thyroid. It is one of the earliest symptoms due to hyperthyroidism (it can occur with much less frequency even in cases of hypothyroidism), to the point that many times the first diagnosis is made by an ophthalmologist during an eye exam. Thyroid ophthalmopathy derives from what is called Basedow-Graves disease and is currently attributed to an infiltration of T lymphocytes within the tissue of the eyelid where the TSH receptor (TSH-R) target of the autoimmune attack is present . The inflammation produced leads to a series of chain reactions involving the eyelid muscle and causing it to increase in volume and contract strongly with the consequent retraction of the eyelid causing the particular symptom

