

Medicalpediaover 7 years ago
#NSFWSensitive content 18+
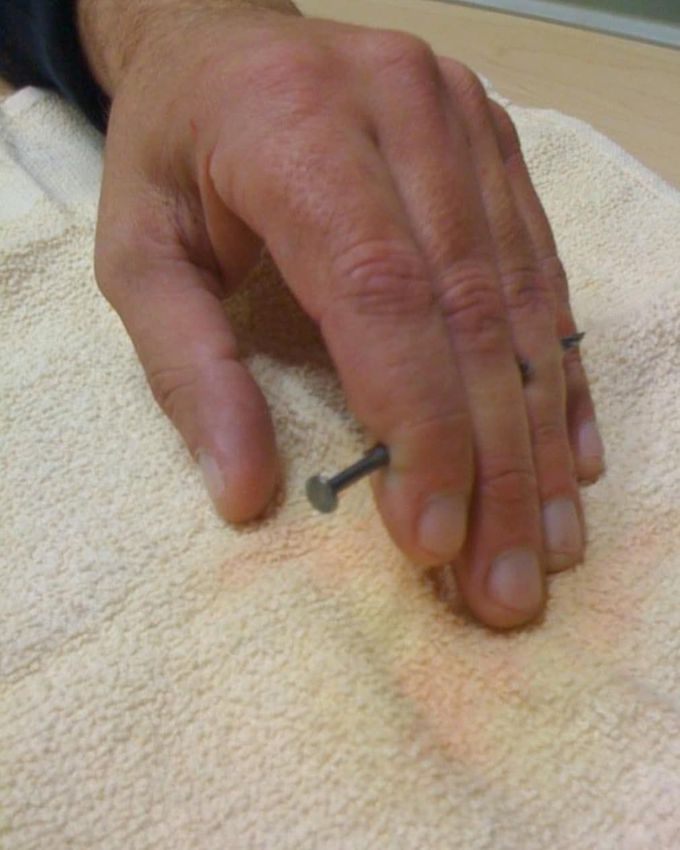
This material contains content which some users might find distrubing⚠️ Nail gun accident, going through three fingers!
Treatment of a retained nail following nail-gun injury adheres to standard principles of wound management. A single dose of intravenous or intramuscular antibiotics is often administered, usually a first-generation cephalosporin to cover skin flora contamination in uncomplicated cases. Regional blocks are usually sufficient for wound exploration and debridement. The wound and surrounding soft tissues are thoroughly irrigated with isotonic sodium chloride solution with or without the addition of antimicrobial agents. Exploration for removal of foreign material and to avoid secondary injury from nail extraction should be considered.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!
Related posts
DERMOGRAPHISM ?WelcomeMental and physical health are interconnected. We, as a society, need to work on emphasizing the importance of the two. This would prevent people developing physical and mental diseases at earlier and earlier ages.Marfan syndrome
Hemodynamic stimuli&nonhemodynamic stimuliEffects of sugar on teethSuturing
Hemodynamic stimuli&nonhemodynamic stimuliEffects of sugar on teethSuturing



