

Treatment for pulmonary effusion
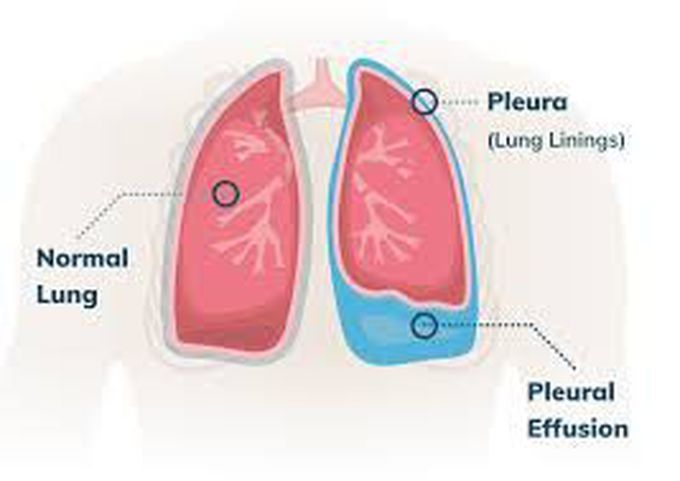
How is pleural effusion treated? Treatment of pleural effusion is based on the underlying condition and whether the effusion is causing severe respiratory symptoms, such as shortness of breath or difficulty breathing. Diuretics and other heart failure medications are used to treat pleural effusion caused by congestive heart failure or other medical causes. A malignant effusion may also require treatment with chemotherapy, radiation therapy or a medication infusion within the chest. A pleural effusion that is causing respiratory symptoms may be drained using therapeutic thoracentesis or through a chest tube (called tube thoracostomy). For patients with pleural effusions that are uncontrollable or recur due to a malignancy despite drainage, a sclerosing agent (a type of drug that deliberately induces scarring) occasionally may be instilled into the pleural cavity through a tube thoracostomy to create a fibrosis (excessive fibrous tissue) of the pleura (pleural sclerosis). Pleural sclerosis performed with sclerosing agents (such as talc, doxycycline, and tetracycline) is 50 percent successful in preventing the recurrence of pleural effusions.
Living with Pulmonary Fibrosis (PF) was one of the hardest experiences of my life. The breathlessness, the fatigue, and the fear of the future weighed on me every single day. I had tried so many treatments and medications, but nothing seemed to stop the disease from progressing.Out of both hope and desperation, I came across NaturePath Herbal Clinic. At first, I was skeptical but something about their natural approach and the stories I read gave me the courage to try one more time.I began their herbal treatment program, and within a few weeks, I noticed small changes easier breathing, more energy, and a clearer mind. Over themonths, those improvements became more and more obvious. Today, I can truly say my life has changed. My lungs feel stronger, and my quality of life has returned in ways I didn’t think were possible.This isn’t just a testimony it’s a heartfelt recommendation to anyone struggling with PF or other chronic conditions. Don’t give up hope. I’m so grateful I gave NaturePath Herbal Clinic a chance. Visit their website to learn more: www.naturepathherbalclinic.com info@naturepathherbalclinic.com


