

Treatment for tacycardia
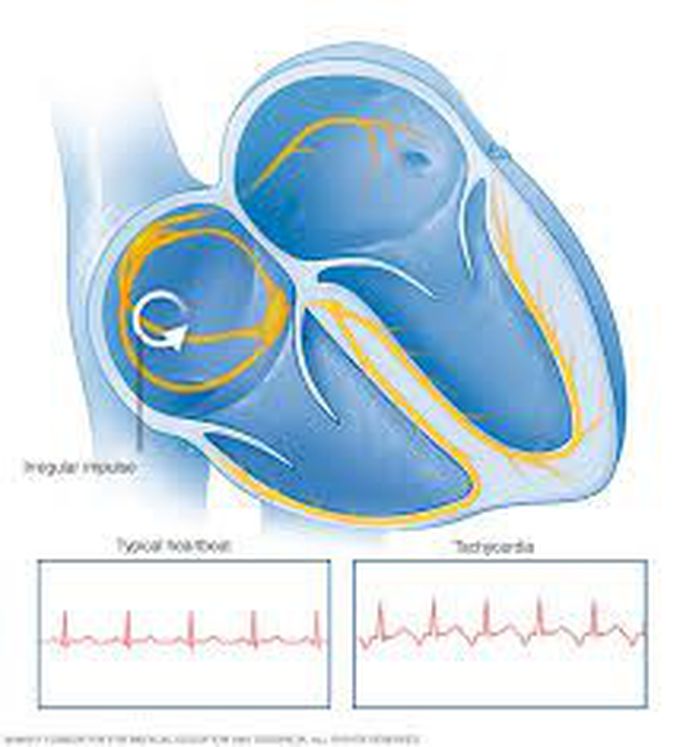
Treatment The goals of tachycardia treatment are to slow a rapid heartbeat when it occurs and to prevent future episodes of a fast heart rate. If another medical condition is causing tachycardia, treating the underlying problem may reduce or prevent episodes of a fast heartbeat. Slowing a fast heart rate A fast heart rate may correct itself. But sometimes medication or other medical treatments are needed to slow down the heartbeat. Ways to slow a fast heart rate include: Vagal maneuvers. Vagal maneuvers include coughing, bearing down as if having a bowel movement and putting an ice pack on the face. Your health care provider may ask you to perform these specific actions during an episode of a fast heartbeat. These actions affect the vagus nerve, which helps control the heartbeat. Medications. If vagal maneuvers don't stop the fast heartbeat, medication may be needed to restore the heart rhythm. Cardioversion. This medical procedure is usually done by sending electric shocks to the heart through sensors (electrodes) placed on the chest. The shock affects the heart's electrical signals and restores a normal heartbeat. Cardioversion is generally used when emergency care is needed or when vagal maneuvers and medications don't work. It's also possible to do cardioversion with medications. Preventing future episodes of a fast heart rate The treatment of tachycardia involves taking steps to prevent the heart from beating too fast. This may involve medication, implanted devices, or other surgeries or procedures. Medications. Drugs to control the heart rate and restore a normal heart rhythm are typically prescribed for most people with tachycardia. Catheter ablation. In this procedure, a health care provider threads one or more thin, flexible tubes (catheters) through an artery, usually in the groin, and guides them to the heart. Sensors (electrodes) on the tip of the catheter use heat or cold energy to create tiny scars in the heart to block irregular electrical signals and restore the heart rhythm. It's often done when an extra signaling pathway is responsible for an increased heart rate. Catheter ablation doesn't require surgery to access the heart, but it may be done at the same time as other heart surgeries. Pacemaker. A pacemaker is a small device that's surgically implanted under the skin in the chest area. When the device senses an irregular heartbeat, it sends an electrical pulse that helps the heart resume the correct rhythm. Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD). Your health care provider may recommend this device if you're at high risk of developing ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. An ICD is a battery-powered unit that's implanted under the skin near the collarbone — similar to a pacemaker. The ICD continuously monitors
Best Probiotics for Women 2025: What's the Hype?The major determinants of cardiac function include all the following EXCEPT a. Heart rate b. Left end diastolic volume c. Cardiac contractility d. Afterload E. Stroke volume
Left and Right Bundle Branch Block: ECG Made EasyVentricular Fibrillation (V-Fib) ECG Interpretation Nursing Heart Rhythms NCLEX ACLSElectrocardiogram (ECG) - Normal sinus rhythm (NSR): Clinical Nursing CareBlue Baby Heart Defect: Tetralogy of FallotAngioplasty, Causes, Signs and Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment.Hypertension

