

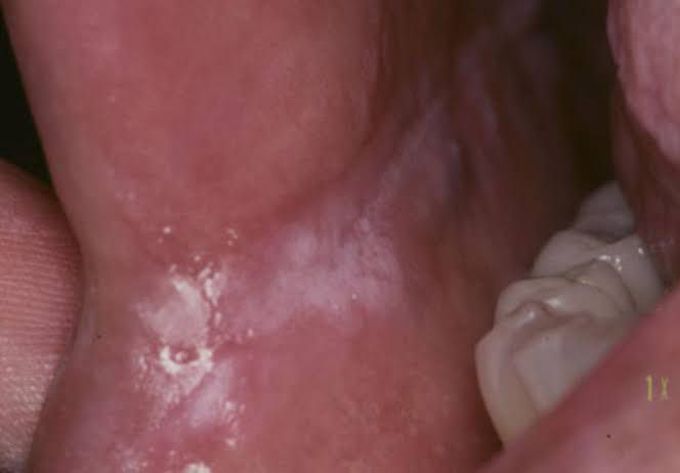
Candidal leukoplakia
Chronic oral candidosis produces a tough, adherent, white plaque (leukoplakia), distinguishable only by biopsy from other leukoplakias. Chronic hyperplastic candidiasis or candidal leukoplakia is a persistent white lesion, characterised histologically (under the microscope) by parakeratosis (increased keratin production) and chronic intra epithelial (within skin cells) inflammation with fungal hyphæ (shape of fungus) invading the superficial layers of the epithelium (skin). Candidal leukoplakia is an uncommon condition found in adults. The epithelium of some leukoplakias is invaded by Candida hyphæ but it is unclear whether the yeasts are secondary invaders or are causally involved in the development / transformation of leukoplakia. The cellular changes often include hyperplasia; however, cellular changes can occur that range from mild dysplasia to invasive carcinoma. C. albicans is the species of fungus that is most commonly found in association with candidal leukoplakia. The Candida biotypes associated with candidal mouths. Candidal leukoplakia may be predisposed to in a minority of patients by: smoking iron and folate deficiencies defective cell-mediated immunity blood group secretor status.

