

Iqraalmost 4 years ago
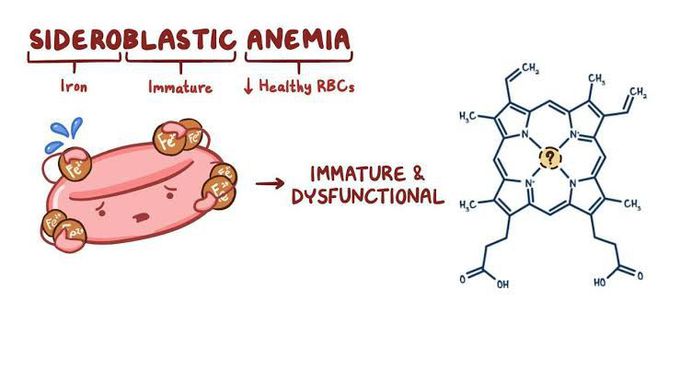
Sideroblastic anemia
Sideroblastic anemia, or sideroachrestic anemia, is a form of anemia in which the bone marrow produces ringed sideroblasts rather than healthy red blood cells (erythrocytes). The most common form of congenital sideroblastic anemia (CSA) is caused by mutation of erythroid-specific 5-aminolevulinate synthase (ALAS2), the first enzyme of heme synthesis in erythroid cells.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!
Related posts
Life cycle of Red Blood cellsLifespan of RBCsBone Marrow Necrosis in Acute Monoblastic LeukemiaSideroblastic AnemiaShelf Life of RBCsBone Marrow Section HistologyCharacteristics of RBCs in different types of anemias.(1)Characteristics of RBCs in different types of anemias.(2)Characteristics of RBCs in different types of anemias.(3)Characteristics of RBCs in different types of anemias.(4)

