

Celiac disease
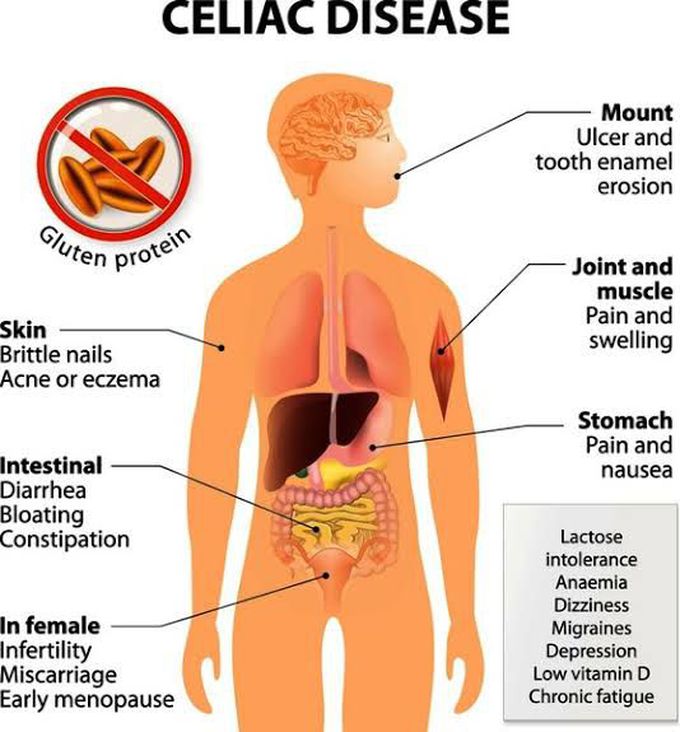
What is coeliac disease? Coeliac disease is an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakes healthy cells for harmful ones and produces antibodies which result in the small intestine becoming inflamed and less able to absorb nutrients. It can cause a range of symptoms including diarrhoea, abdominal pain and bloating, as well as non-gut related symptoms. The condition is caused by an adverse reaction to gluten, a dietary protein found in three types of cereal: wheat, barley and rye (oats may also be contaminated with gluten, unless labelled gluten-free). The surface of the intestine is covered with millions of tiny projections known as villi which increase its surface area and help with more efficient food digestion. However, in coeliac disease, the damage caused to the lining of the small intestine flattens the villi which can result in malabsorption.

