

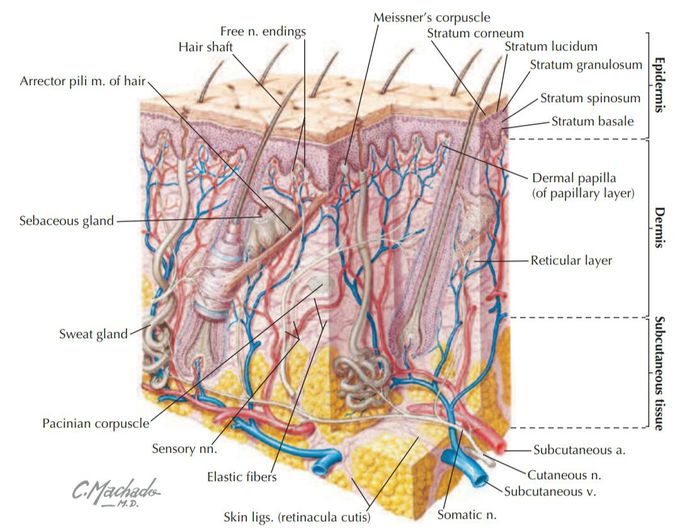
#chapter_1 #introduction_To_The_Human_Body #SKIN *The skin is the largest organ in the body, accounting for about 15% to 20% of the total body mass, and has the following functions: • Protection: against mechanical abrasion and in immune responses, as well as prevention of dehydration. • Temperature regulation: largely through vasodilation, vasoconstriction, fat storage, or activation of sweat glands. • Sensations: to touch by specialized mechanoreceptors such as pacinian and Meissner’s corpuscles; to pain by nociceptors; and to temperature by thermoreceptors. • Endocrine regulation: by secretion of hormones, cytokines, and growth factors, and by synthesis and storage of vitamin D. • Exocrine secretions: by secretion of sweat and oily sebum from sebaceous glands. *The skin consists of two layers: • Epidermis: is the outer protective layer consisting of a keratinized stratiied squamous epithelium derived from the embryonic ectoderm. • Dermis: is the dense connective tissue layer that gives skin most of its thickness and support, and is derived from the embryonic mesoderm. *Fascia: is a connective tissue sheet that may contain variable amounts of fat. It can interconnect structures, provide a conduit for vessels and nerves, and provide a sheath around structures that permits them to slide over one another easily. *Supericial_fascia: is attached to and lies just beneath the dermis of the skin and can vary in thickness and density; it acts as a cushion, contains variable amounts of fat, and allows the skin to glide over its surface. *Deep_fascia: usually consists of a dense connective tissue, is attached to the deep surface of the supericial fascia, and often ensheathes muscles and divides them into functional groupings. *Common injuries to the skin include abrasions, cuts, and burns. Burns are classiied as follows: • First_degree: burn damage that is limited to the supericial layers of the epidermis; termed a superficial burn, clinically it causes erythema. • Second_degree: burn damage that includes all of the epidermis and extends into the superficial dermis; termed, it causes blisters but spares the hair follicles and sweat glands. • Third_degree: burn damage that includes all the epidermis and dermis and may even involve the subcutaneous tissue and underlying deep fascia and muscle. ____________ ✍رضا جعليك
living with Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) was a daily struggle. I constantly felt out of breath, even while resting. Simple activities like walking to the mailbox or climbing a few stairs left me drained and gasping for air. The medications I was on gave temporary relief, but the side effects made it even harder to cope.In a moment of hope and honestly, exhaustion I decided to try the herbal program from NaturePath Herbal Clinic. At first, I wasn’t sure what to expect. But after a few months on the treatment, I began to notice steady improvements. My breathing became less laboured, my coughing reduced, and I felt more energetic throughout the day.What makes this program different is that it’s completely natural and gentle on the body, unlike many pharmaceutical treatments I had tried in the past. I didn’t experience any negative side effects, and the improvement in my quality of life has been incredible.I’ve now been on the program for over nine months, and my most recent checkup showed that my condition has sthbilized. For a disease that doctors told me had no cure, this was more than I could have hoped for. I feel like I’ve been given a second chance at life.If you or a loved one is battling ILD and struggling to find relief, I highly encourage you to explore this option. It has truly made a difference in my life.their website is www.naturepathherbalclinic.com
https://www.facebook.com/PrimalTRTOfficial/Women’s Reproductive Health & Daily WellnessFlexiLeafhttps://www.facebook.com/HumeHealthBodyPodOfficial/Pulsar Vexline Review 2026 - Legit Or Scam Trading Platform? Fact CheckGelatine Sculpt | Official WebsiteBurnSlim Official | Support Your Weight Management Journey



