

Hiba Saleemover 4 years ago
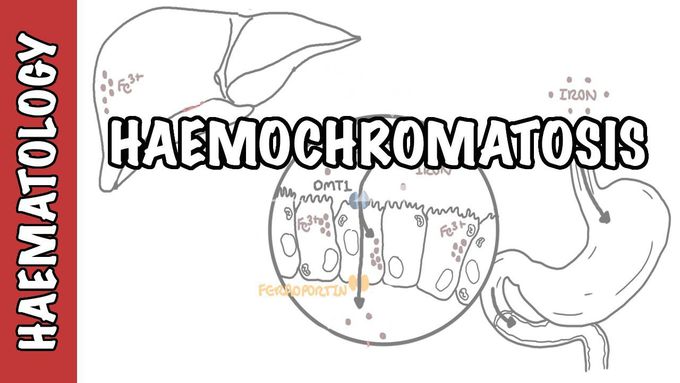
Pathogenesis of Hemochromatosis
Watch this video if you learn about the pathogenesis of Hemochromatosis and the diagnostic options available to identify patients with this condition. 0:00 Introduction 0:36 Pathogenesis 9:47 Diagnosis
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

