

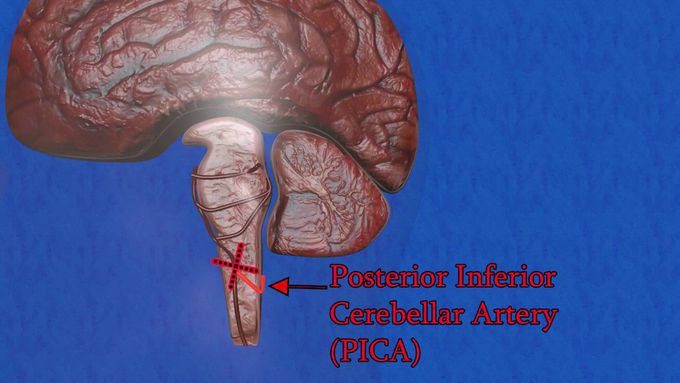
Wallenberg syndrome (Lateral medullary syndrome)
Infarction involving the lateral medulla (Wallenberg syndrome) is usually caused by occlusion of the vertebral artery. As medulla is the site of origin of lower cranial nerves and also provides conduit for tracts between the spinal cord and higher centres, it can present with a variety of features. They include: 1. Vertigo, nausea, vomiting, and nystagmus result from involvement of the vestibular nuclei. 2. Hoarseness and dysphagia are caused by involvement of the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus (X) nerve, nucleus solitarius, and nucleus ambiguous. 3. Ipsilateral Horner syndrome, limb ataxia, and loss of all sensation over the face and of light touch and position sense in the limbs are due to involvement of the descending sympathetic tract, inferior cerebellar peduncle, and spinal nucleus and tract of the trigeminal (V) nerve. 4. Contralateral impaired pin and temperature sense in the limbs results from involvement of the spinothalamic tract.

