

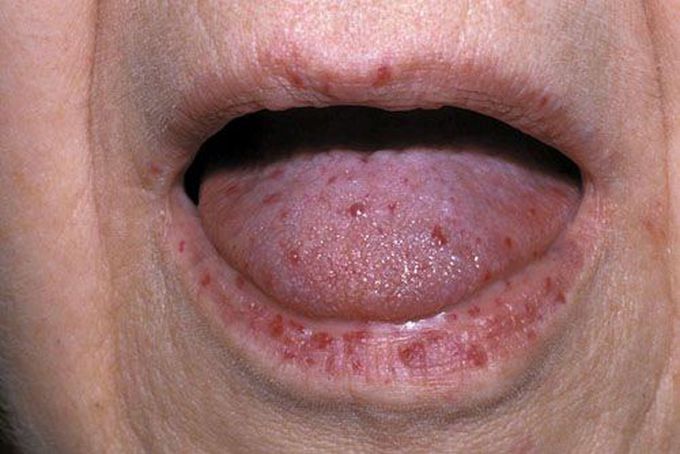
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia
Also known as Osler-Weber-Rendu Disease, Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT) is an autosomal dominant disorder. It is characterized by abnormal vasculature in skin, mucous membranes, and solid organs. Multiple arteriovenous malformation may also be present. The patient with HHT usually presents with epistaxis and chronic gastrointestinal tract bleeding. The management plan aims at reducing the bleeding. Surgical intervention is usually done in order to remove arteriovenous malformations. Iron supplementation is required to anemia secondary to chronic GIT bleeding. Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hereditary_hemorrhagic_telangiectasia#Signs_and_symptoms Image via: https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/hematology-and-oncology/bleeding-due-to-abnormal-blood-vessels/hereditary-hemorrhagic-telangiectasia

