

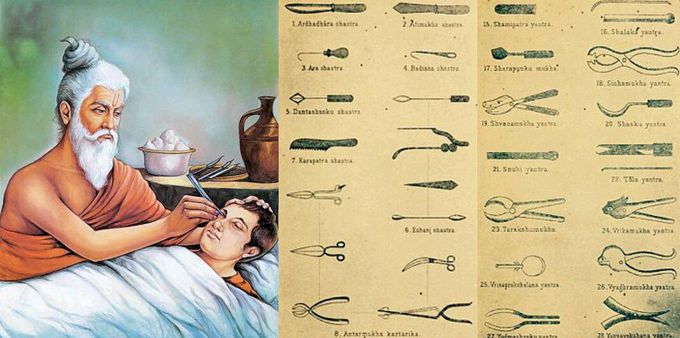
SUSHRUTA
Sushruta, was an ancient Indian physician during 1500 BCE to 1000 BCE, known as the main author of the Suśruta-saṃhitā .He is widely considered as the "father of surgery". The Suśruta-saṃhitā, contains descriptions of 1,120 illnesses, 700 medicinal plants, 64 preparations from mineral sources and 57 preparations based on animal sources. The text discusses surgical techniques of making incisions, probing, extraction of foreign bodies, alkali and thermal cauterization, tooth extraction, excisions, and trocars for draining abscess, draining hydrocele and ascitic fluid, removal of the prostate gland, urethral stricture dilatation, vesicolithotomy, hernia surgery, caesarian section, management of haemorrhoids, fistulae, laparotomy and management of intestinal obstruction, perforated intestines and accidental perforation of the abdomen with protrusion of omentum and the principles of fracture management, viz., traction, manipulation, apposition and stabilization including some measures of rehabilitation and fitting of prosthetic. It enumerates six types of dislocations, twelve varieties of fractures, and classification of the bones and their reaction to the injuries, and gives a classification of eye diseases including cataract surgery.

