

Hosamover 7 years ago
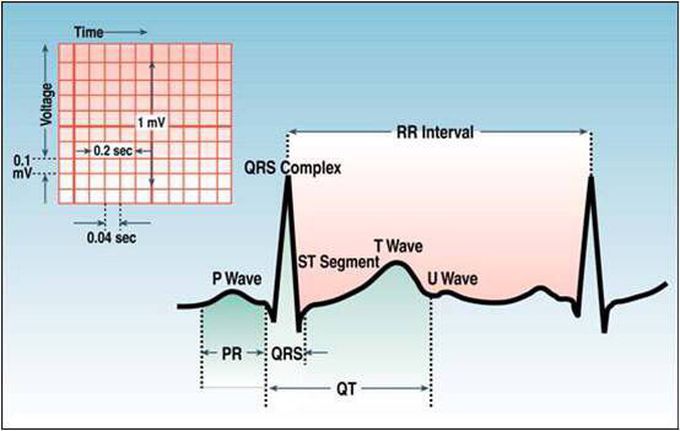
The U Wave
It’s is wave on an electrocardiogram that is not always seen. It is typically small, jand, by definition, follows the T wave. U waves are thought to represent repolarization of the papillary muscles or Purkinje fibers. • Interpretation Prominent U waves are most often seen in hypokalemia, but may be present in hypercalcemia, thyrotoxicosis, or exposure to digitalis, epinephrine, and Class 1A and 3 antiarrhythmics, as well as in congenital long QT syndrome, and in the setting of intracranial hemorrhage. An inverted U wave may represent myocardial ischemia or left ventricular volume overload. A U-wave could normally be seen in younger, athletic individuals.


