

Dr. Sumana Chowdhury10 months ago
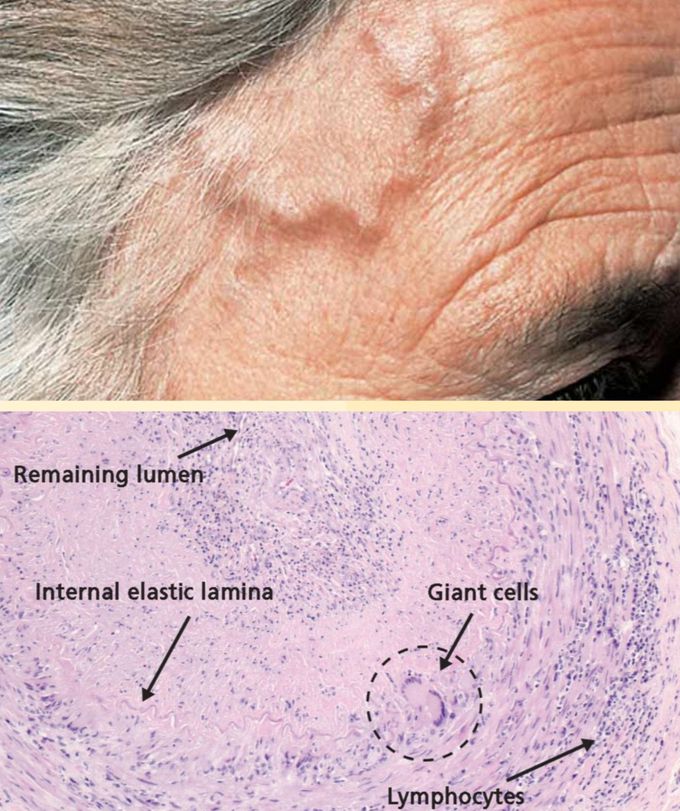
Temporal Arteritis
Also known as Giant cell arteritis. The most common artery involved here is the Superficial Temporal Artery. Pathogenesis: There is chronic inflammation leading to tissue destruction and healing by fibrosis. As a result, there is a decrease in size of the lumen. Symptoms: Headache in the temporal region. Thickened cord like superficial temporal artery may be felt. Jaw claudication if maxillary and facial artery are involved. Blindness if ophthalmic artery is involved. Biopsy shows giant cells, fragmented internal elastic lamina and granuloma. Treatment: Steroids.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

