

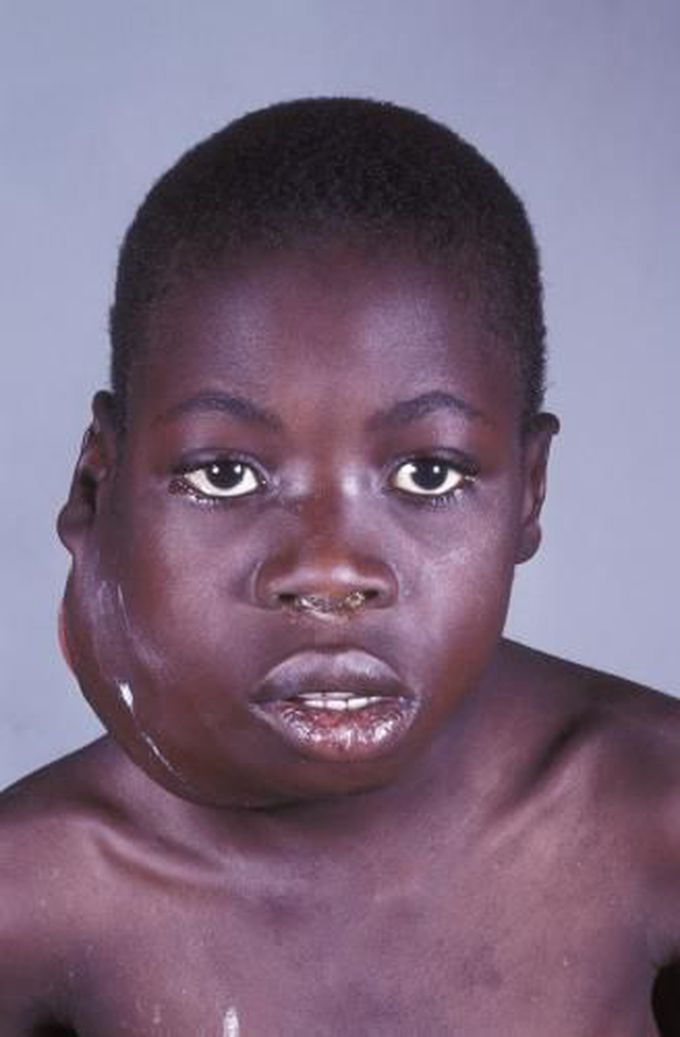
Burkitt Lymphoma
One of the types of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma is Burkitt lymphoma. It is a fast-growing tumor characterized by impaired immunity which is often fatal. In underdeveloped countries, Burkitt lymphoma occurs in young children as a complication of infectious mononucleosis secondary to EBV infection or malaria. It can also occur in individuals with HIV. Burkitt lymphoma can arise in jaw, facial bones, breast, ovaries, and gastrointestinal tract. It can also spread to central nervous system. Prompt diagnosis is imperative due to its fast spread. Intense chemotherapy can limit the spread of disease thereby increasing life expectancy. Reference: https://www.webmd.com/cancer/lymphoma/burkitt-lymphoma-prognosis-diagnosis-treatments Image via: https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/hematology-and-oncology/lymphomas/burkitt-lymphoma
It's also associated with genetic defects like t(8; 22), t(8; 14), t(2; 8 ). These defects increase c-myc concentration. Which responsible for increases in mitosis and so cell proliferation accelerate.
Living with HIV was one of the hardest experiences of my life. The fatigue, the emotional toll, and the uncertainty about the future weighed on me every single day. I had tried many treatments and medications, but nothing seemed to restore my health or energy the way I hoped.Out of both hope and desperation, I came across NaturePath Herbal Clinic. At first, I was skeptical but something about their natural approach and the powerful stories I read gave me the courage to try one more time.I began their herbal treatment program, and within a few weeks, I noticed small but meaningful changes more energy, better sleep, and a stronger immune system. Over the months, those improvements only grew. Today, I can truly say my life has changed. I feel healthier, more balanced, and finally in control of my well-being again.This isn’t just a testimony it’s a heartfelt recommendation to anyone living with HIV or any chronic condition. Don’t give up hope. I’m so grateful I gave NaturePath Herbal Clinic a chance. Visit their website to learn more: www.naturepathherbalclinic.com Email: info@naturepathherbalclinic.com



